User Guide
Hello NUS School of Computing (SoC) students! Welcome to the User Guide for ModContacts!
TIRED of constantly needing to remember what your NUS friends are up to? ModContacts is a desktop app for keeping track of your peers and the modules that they take so that you can keep in contact with them amidst your journey in NUS!
Table of Contents
- Table of Contents
- About ModContacts
- Getting Started
-
Features
- Adding a friend:
add - Listing all friends :
list - Editing a friend :
edit - Adding a Module:
add_module - Deleting a Module:
delete_module - Adding a Module Timing:
add_timing - Deleting a Module Timing:
delete_timing - Locating friends by name:
find - Find friends who are free to meet:
find_free_time - Learn more about modules:
list_modules - Find friends with modules:
module_search - Deleting a friend :
delete - Clearing all entries :
clear - Exiting the program :
exit
- Adding a friend:
- FAQ
- Glossary
- Command summary
About ModContacts
Who is ModContacts for?
ModContacts tailored specifically for:
- NUS School of Computing students,
- people who want to keep in touch with their NUS friends easily,
- people who desire academic success by utilising their social connections,
- people quick on the keyboard, tired of moving constantly between the mouse and keyboard
What does ModContacts do?
ModContacts is designed to help School of Computing students:
- Effortlessly keep track of all their friend’s modules and schedules
- Our one-stop solution to keeping track of our friend’s timetables!
- Find out common timings when everyone is free to meet
- Say goodbye to painting when2meets!
- Discover who is taking the same module as you
- No more constantly asking: “hey bro, what mods are you doing this sem?”
What is the Purpose of this User Guide?
Some of you are definitely thinking: What is the point of this User Guide?
The ModContacts User Guide serves as a quick, efficient, all-in-one manual for both new and experienced users.
New Users
It is great to see that you’re interested in using ModContacts!
Head to the Getting Started section and follow the guide to get ModContacts up and running!
Then check out the Tutorial some Features, and the handy Command Summary.
Experienced Users
Head over to the Command Summary, FAQ or Troubleshooting sections.
How should I use this guide?
The guide includes information on how users can effectively navigate the document, clarifies the meaning of icons and formatting used, and provides guidance on understanding features, functions, or commands. These can be quickly referenced from the Table of Contents.
Conventions
| Convention | Description |
|---|---|
| Link | These are links to sections within the user guide |
Command |
Commands are represented with this text |
| These are tips that might be useful during the operation of ModContacts | |
| These are warnings to take note of during the operation of ModContacts | |
m/FIELD |
These are required fields in a command |
[i/FIELD] |
These are optional fields in a command |
Getting Started
Prerequisites
For ModContacts to work, you need to have Java 11 or above installed on your computer!
Follow this guide for your OS of choice:
Quick start
-
Ensure you have Java
11or above installed in your computer from the Prerequisites Section. -
Download the latest
modcontacts.jarfrom here. -
Opening the app:
-
If you are using Windows: Simply double-click on
modcontacts.jarwithin your file explorer and a GUI similar to what is shown below should appear! -
If you are using MacOS / Linux: Open a terminal window. Navigate to the folder containing
modcontacts.jarusing thecd [relative/absolute folder path]command. Then runjava -jar modcontacts.jar.
-
If you are using Windows: Simply double-click on
On First launch, the app should look like this:
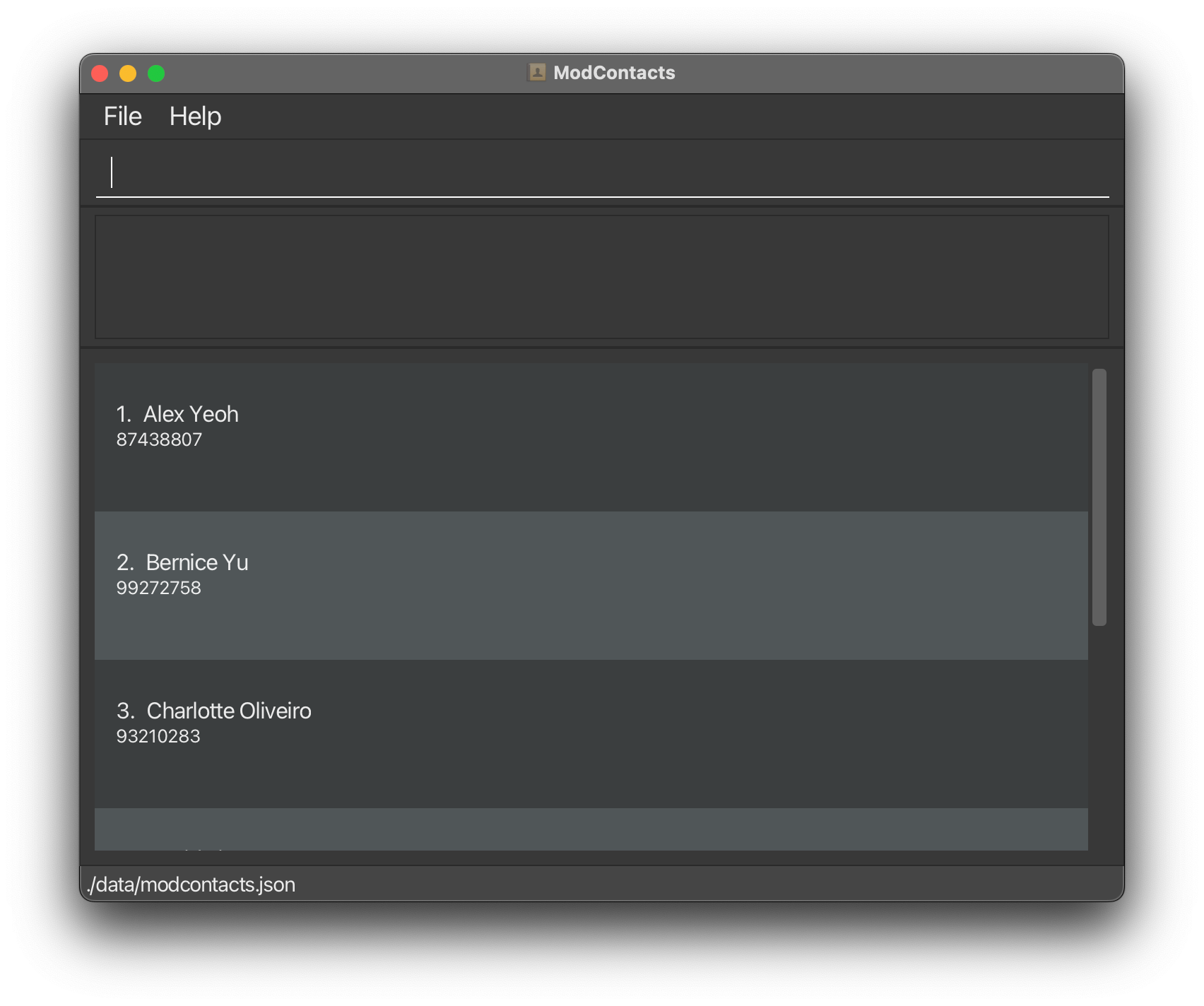
Usage
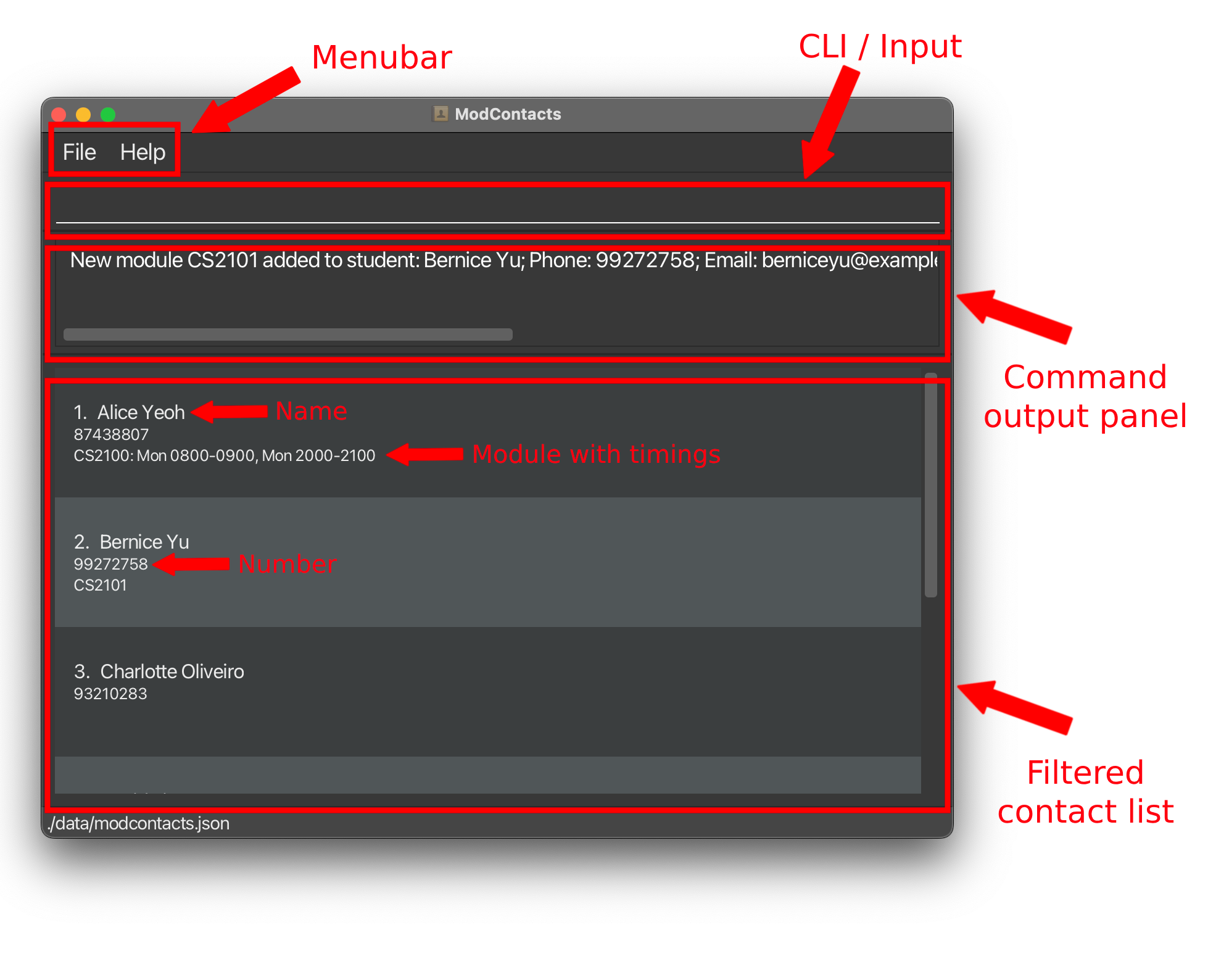
- Menubar: This is where you will find the
FileandHelpoptions.-
Fileprovides you a menu, which contains an option to exit the app. -
Helpshows you a pop-up, using which you can access the User Guide.
-
- CLI / Input: This is where you enter commands to interact with the app.
- Command output panel: This is where you would see the output of the commmand that you have entered in the CLI.
- Filtered contact list: This is the main information panel of the app. Here you will see a list of your contacts, that you can filter using commands.
- Filtering the list is done using commands like
findandfind_free_time, which change the filtered contact list by reducing the number of contacts displayed. - After this, when you use other commands like
edit, the command inputs are based on the contacts that are currently visible in the filtered contact list. You will learn more about this in a later section.
- Filtering the list is done using commands like
- Name, Number, Module with timings: These are the details for a particular contact in the filtered contact list.
What is a Command?
A command is what you type into the app to execute your intentions (Adding a Friend or a Module)!
Here are some examples of commands that you’d be using:
-
add n/Aditya p/98765432 e/adityab4@u.nus.edu a/2 College Ave West, Singapore 138607 -
add_module i/1 m/MA2001 -
delete_module i/2 m/CS1231S
You may notice a pattern here, and here is a rough breakdown of what a command composes of. Let’s use the first example!
add n/Aditya p/98765432 e/adityab4@u.nus.edu a/2 College Ave West, Singapore 138607
Our command composes of:
-
A Command Word (
add)This is the first word of your command that carries the intention of your action! Examples would be using
addwhen you want to add aFriend,add_modulewhen you want to add aModuleto yourFriend, so on and so forth! -
Prefixes (
n/Aditya p/98765432 e/adityab4@u.nus.edu a/2 College Ave West, Singapore 138607)Prefixes are additional information that you add to your command. For example, when adding a friend you would want to add their name and their email.
We can use Prefixes to accomplish this! They are usually marked with an unique identifier (
n/for name,p/for phone number, etc). You can then add your values after the identifiers! (Adityais the value supplied for the name when you typen/Aditya).(P.S) Different commands have different prefixes! Check out the Features section to see what prefixes exist for each command.
Summary
In summary, what this command (add n/Aditya p/98765432 e/adityab4@u.nus.edu a/2 College Ave West, Singapore 138607)
does is that it adds a Friend whose name is Aditya, has a phone number 98765432, has an email is adityab4@u.nus.edu and stays at the address 2 College Ave West, Singapore 138607.
![]() Notes about the command format:
Notes about the command format:
-
Words in
UPPER_CASEare the parameters to be supplied by the user.
e.g. inadd n/NAME,NAMEis a parameter which can be used asadd n/John Doe. -
Items in square brackets are optional.
e.gn/NAME [t/TAG]can be used asn/John Doe t/friendor asn/John Doe. -
Items with
… after them can be used multiple times including zero times.
e.g.[t/TAG]…can be used ast/friend,t/friend t/familyetc. -
Parameters can be in any order.
e.g. if the command specifiesn/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER,p/PHONE_NUMBER n/NAMEis also acceptable. -
Extraneous parameters for commands that do not take in parameters (such as
help,list,exitandclear) will be ignored.
e.g. if the command specifieshelp 123, it will be interpreted ashelp. -
If you are using a PDF version of this document, be careful when copying and pasting commands that span multiple lines as space characters surrounding line-breaks may be omitted when copied over to the application.
Refer to the Features below for details of each command.
Tutorial
Lets run through the first few steps of using ModContacts to get you started!
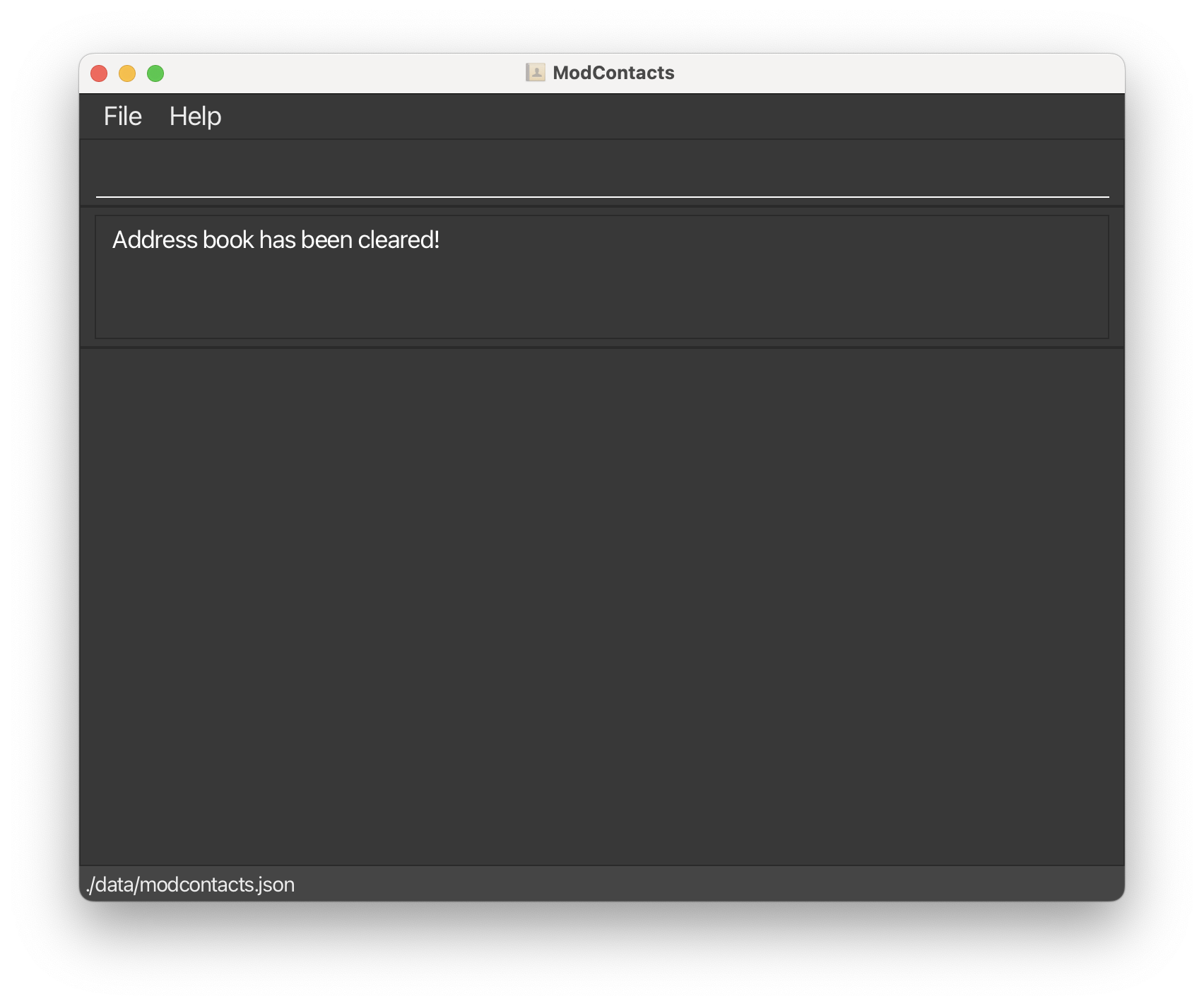
Lets start by clearing the data that comes with the app by default.
- Run the
clearcommand in the input box to clear the data.
Be careful! This will delete all contacts from ModContacts. Since we don’t have any contacts of our own yet, this is a safe command to run.
You should see something like this
- We just had a chat with our friend Taufiq, and found out that he is taking the modules
CS2103TandCS20?next semester. You remember that it’s the Data Structures module but don’t remember the exact module code. Firstly, lets add him to our contacts list. Since he Rock Climbs, lets add these details as tags into the application.
Taufiq’s Details:
| Field | Value |
|---|---|
| Name | Taufiq Mohammed |
| Phone | 98765432 |
| taufiq@taufiq.com | |
| Address | 123, Clementi Road, 123456 |
| Tags | friend, rockClimbing |
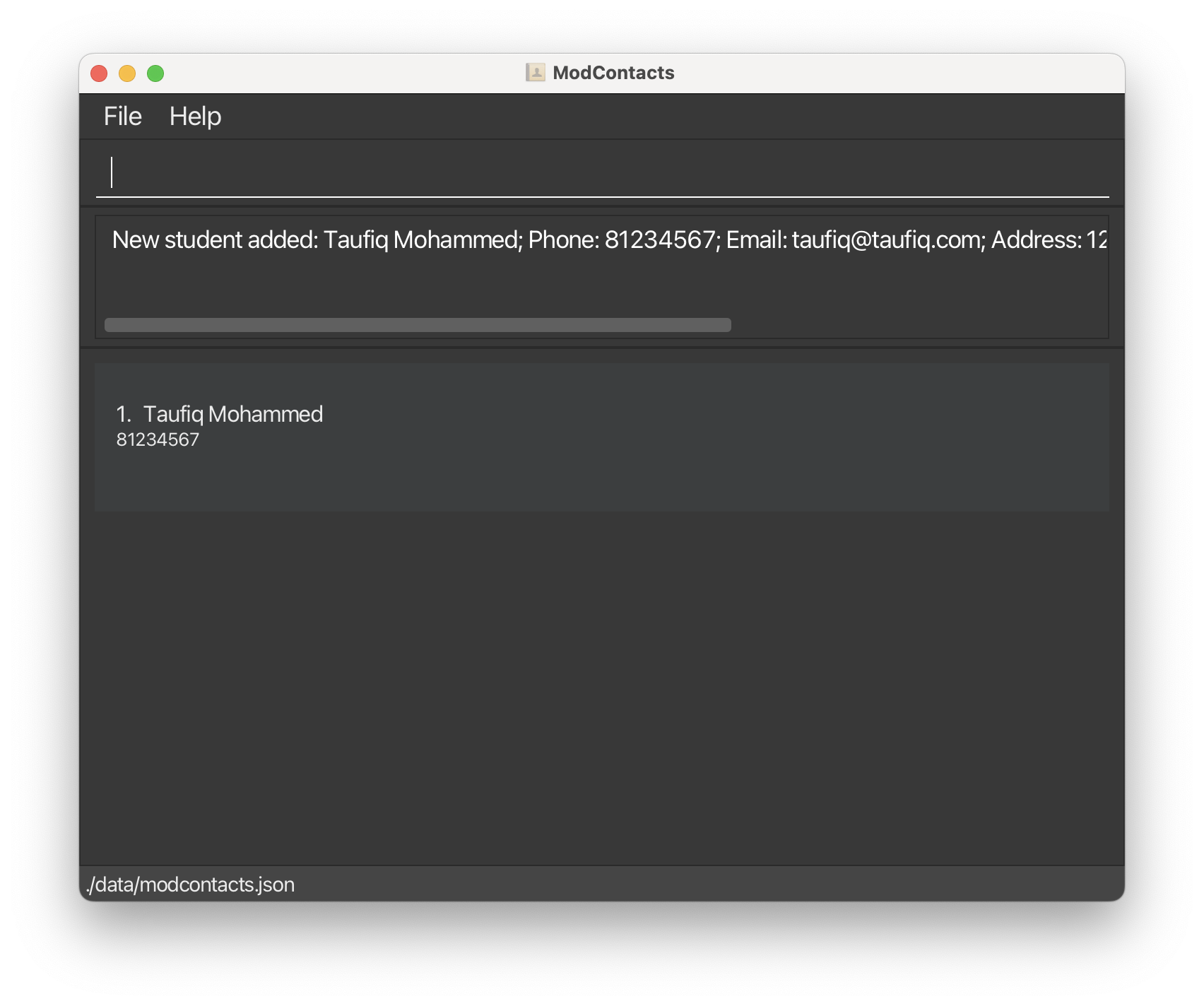
With this details, we’ll run the command
add n/Taufiq Mohammed p/81234567 e/taufiq@taufiq.com a/123, Clementi Road, 123456 t/friend t/rockClimbing
You can add multiple tags for each user. However, spaces in a tag are not supported. You’ll need to add a t/ prefix before each tag also.
- We can now add the module
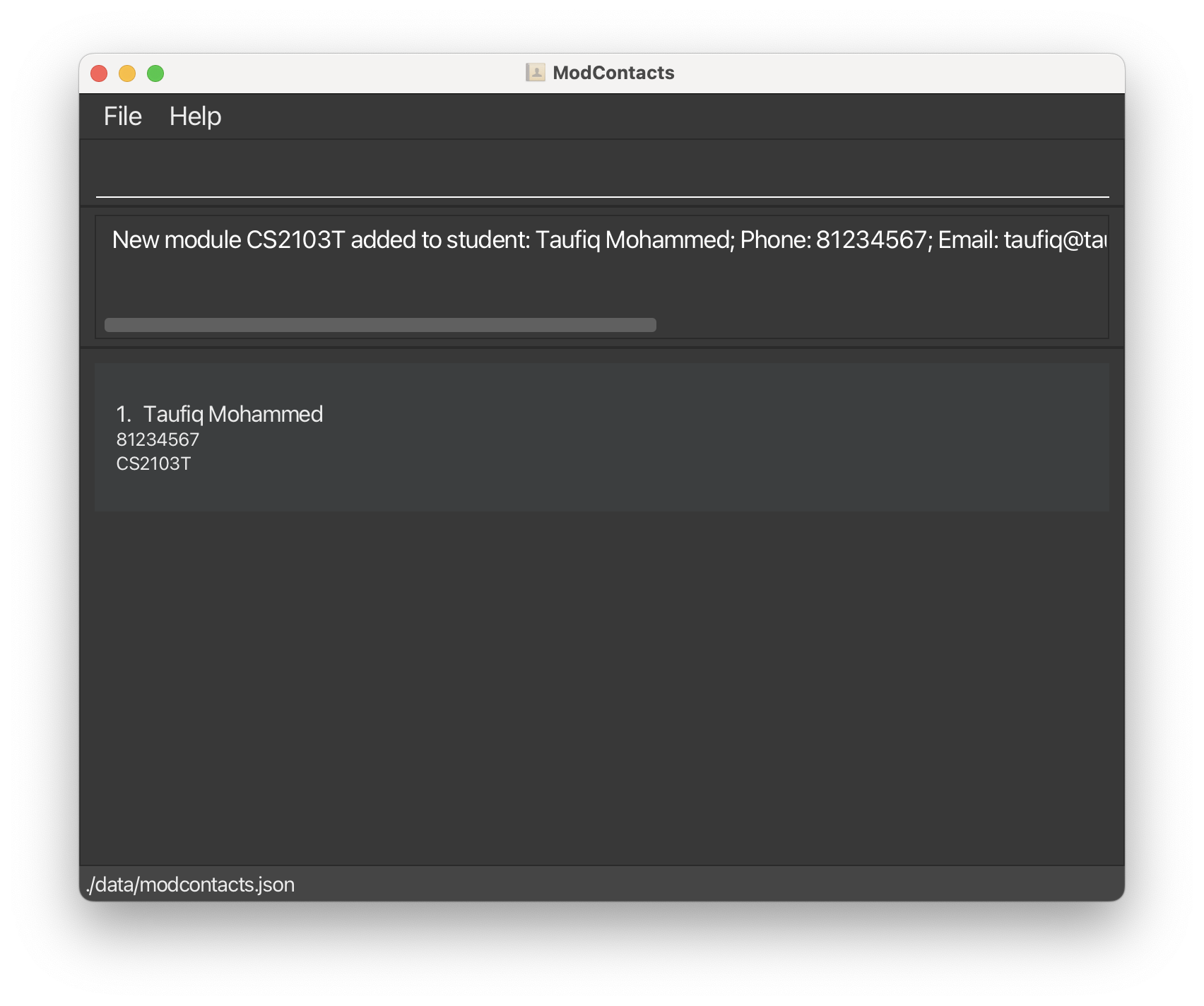
CS2103Tto Taufiq’s list of modules. We’ll use the commandadd_module i/1 m/CS2103Tto add the module to Taufiq’s list of modules.
The 1 in the above command refers to the index of the friend in the list. Since Taufiq is the first friend in the list, he is at index 1.
- Now, since we’re unsure which module Taufiq is taking, we can use the
list_modulescommand to search for the module. We’ll use the commandlist_modules m/CS20to search for modules starting withCS20.
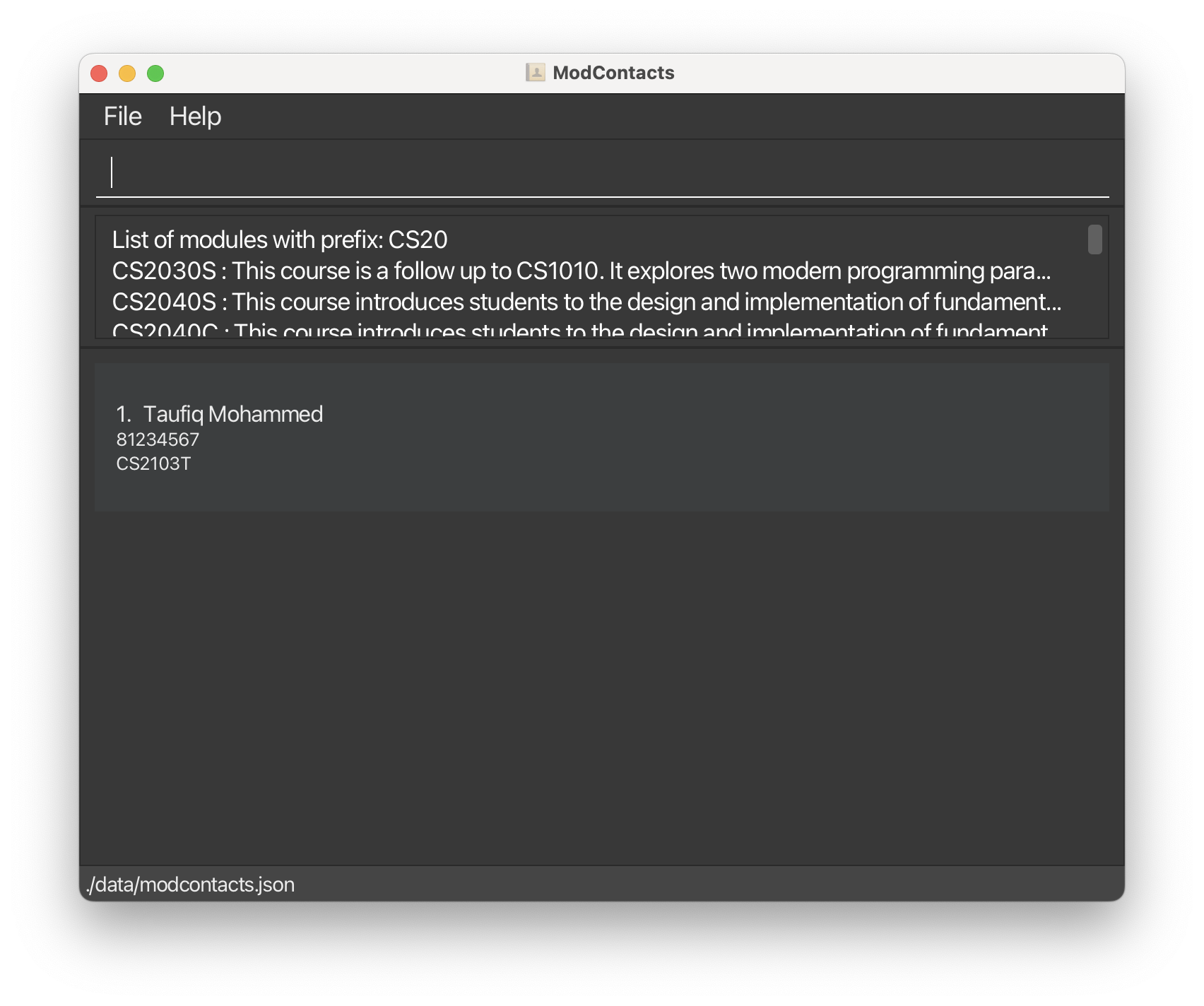
From this, we can read the descriptions and find out that the module we’re looking for is CS2040S. Lets add that to Taufiq. add_module i/1 m/CS2040S.
Do note that if you try to add the same module again to the same person, it will give a warning that the module is already added.
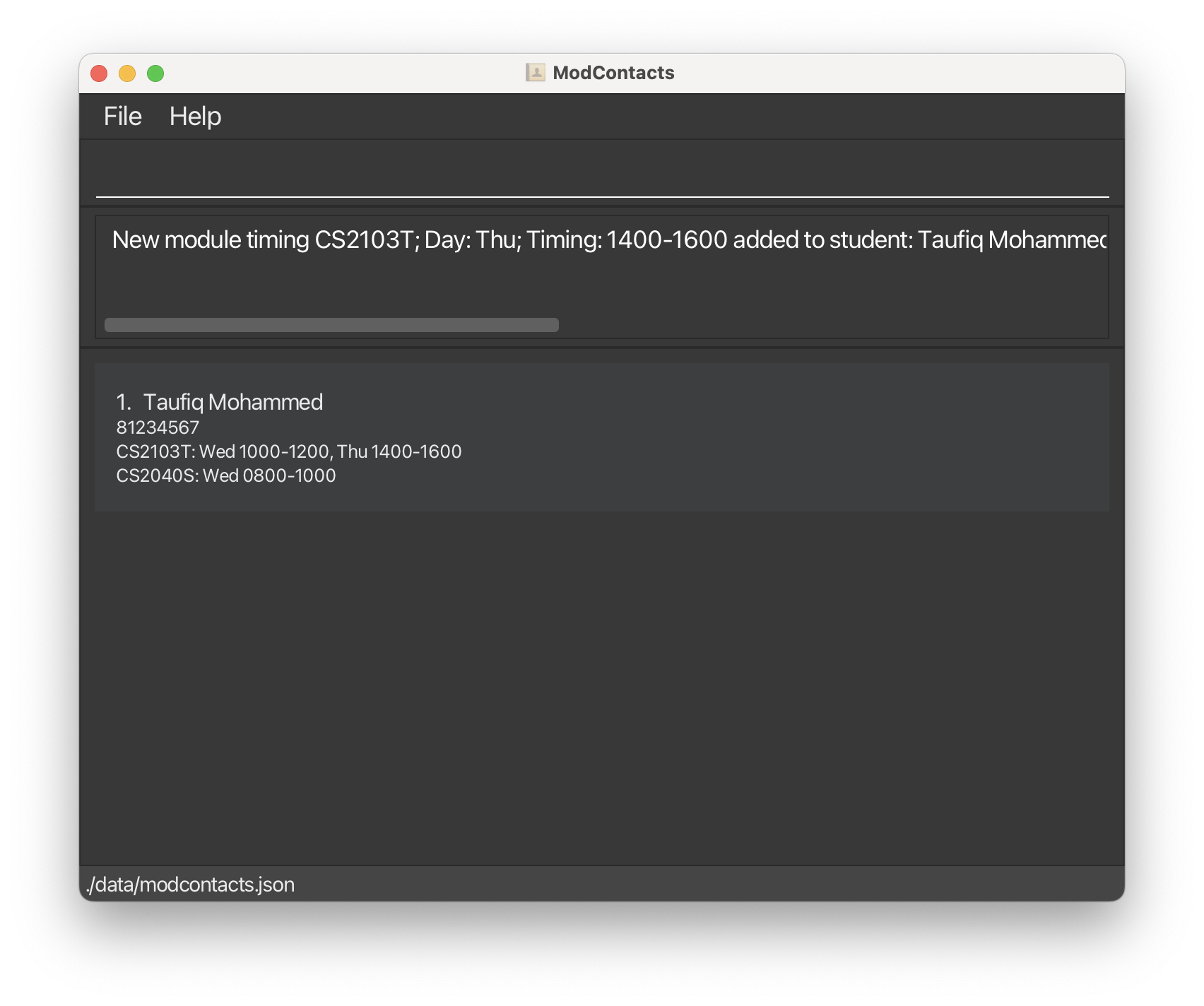
- Suppose you want to add the timing
1600h – 1800hon Wednesday and1400h - 1600hon Thursday to theCS2103Tand0800h - 1000hon Wednesday to theCS2040Smodule Taufiq.
Type the following commands:
add_timing i/1 m/CS2103T d/Wed st/1600 et/1800add_timing i/1 m/CS2103T d/Thu st/1400 et/1600add_timing i/1 m/CS2040S d/Wed st/0800 et/1000
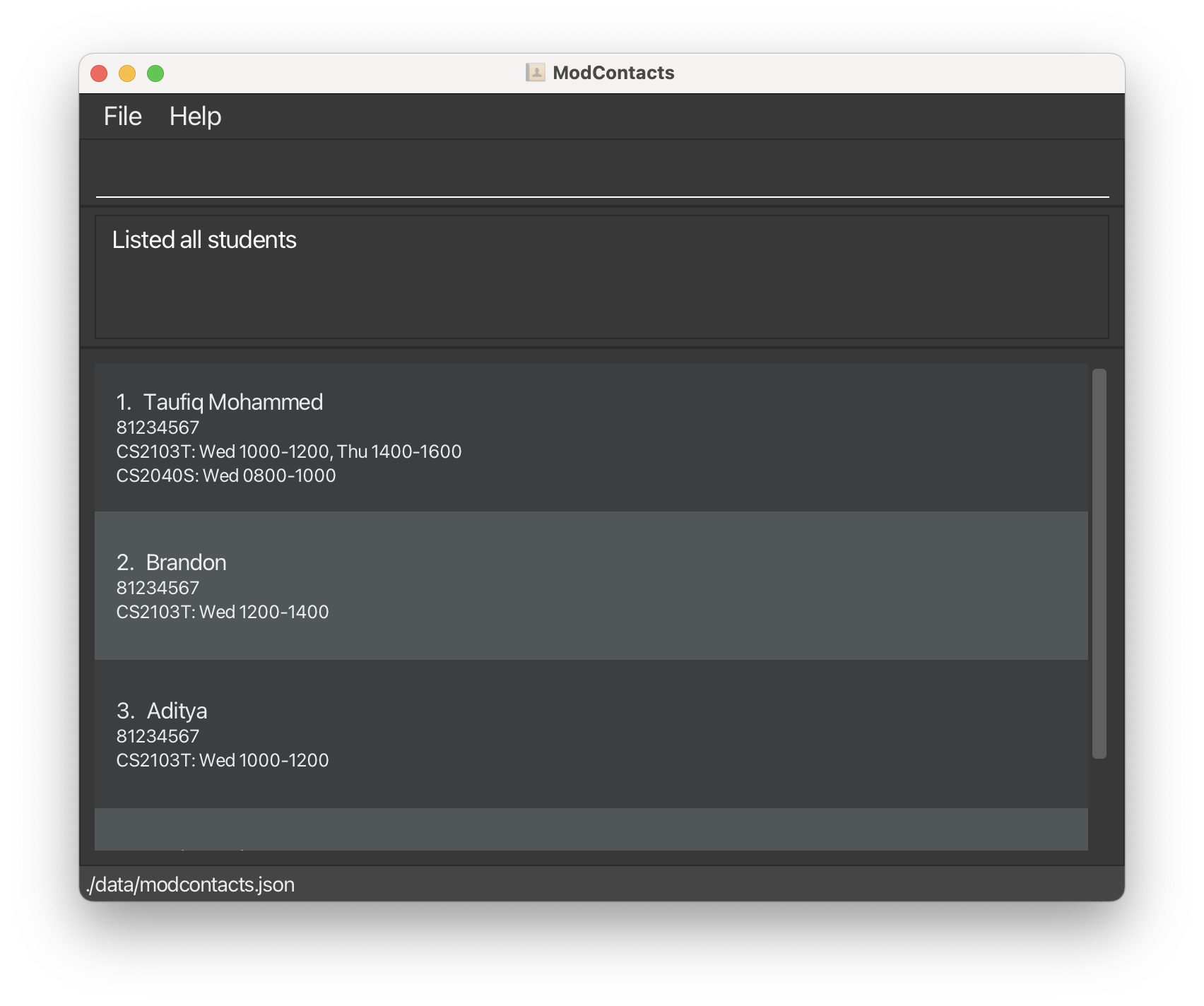
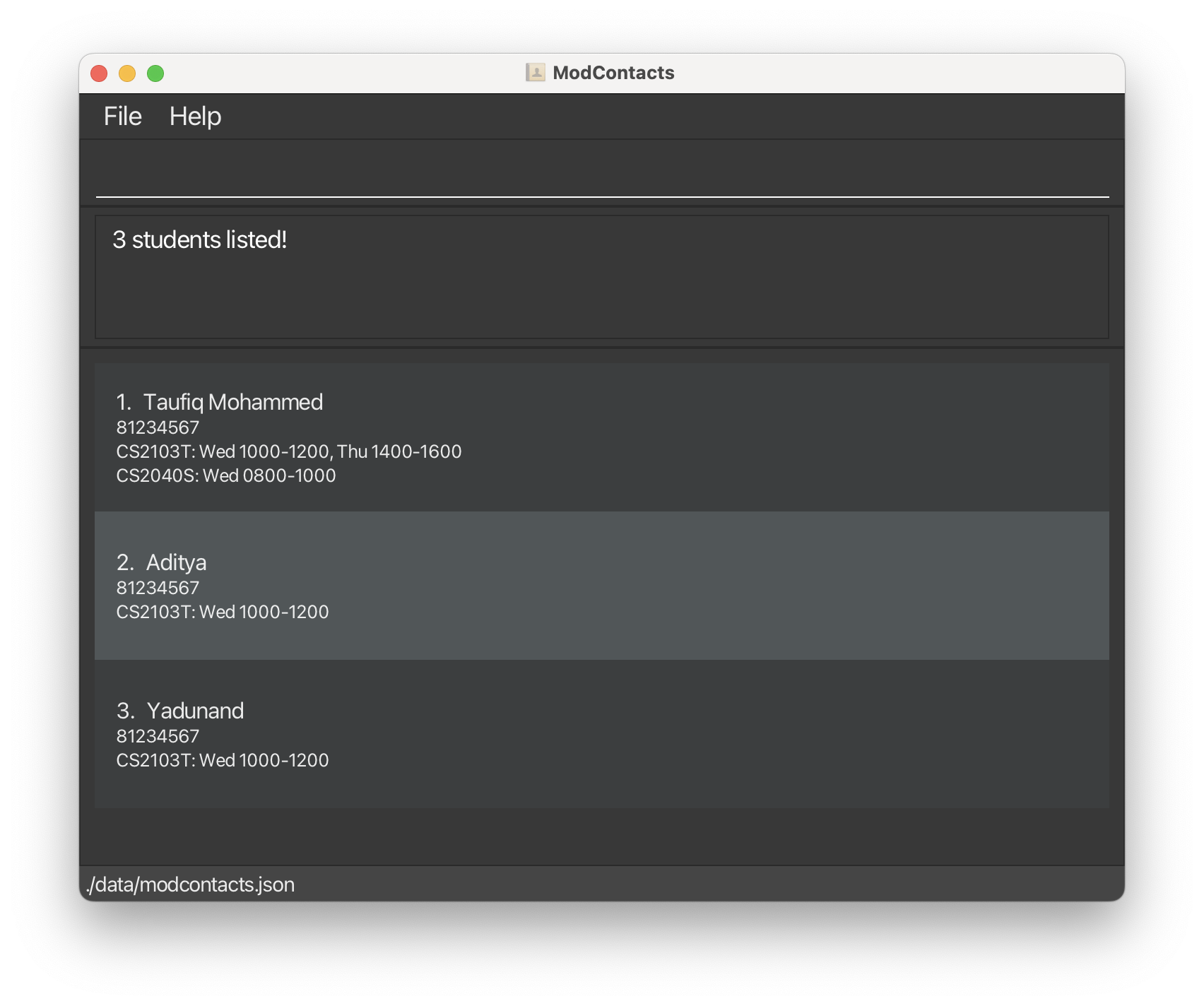
- Now, using the above commands, we can add the rest of our friends, their modules and its timings. You can use the
listcommand to see the entire list of friends in the application
- Suppose that you’re looking for friends to eat lunch with on Wednesday from
1200 - 1400. With the commandfind_free_time d/Wed st/1200 et/1400, you can find friends who are free during that period.
This tutorial is not exhaustive and is just a preview of some of the commands you can use in ModContacts. For a full list of commands with a detailed explanation, refer to the Features section and for a quick overview of all the commands available, you can look at the Command Summary.
Features
Adding a friend: add
Adds a friend to the mod contacts list.
Format: add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]…
Examples:
add n/John Doe p/98765432 e/johnd@example.com a/John street, block 123, #01-01add n/Betsy Crowe t/friend e/betsycrowe@example.com a/Newgate Prison p/1234567 t/criminal
Before command
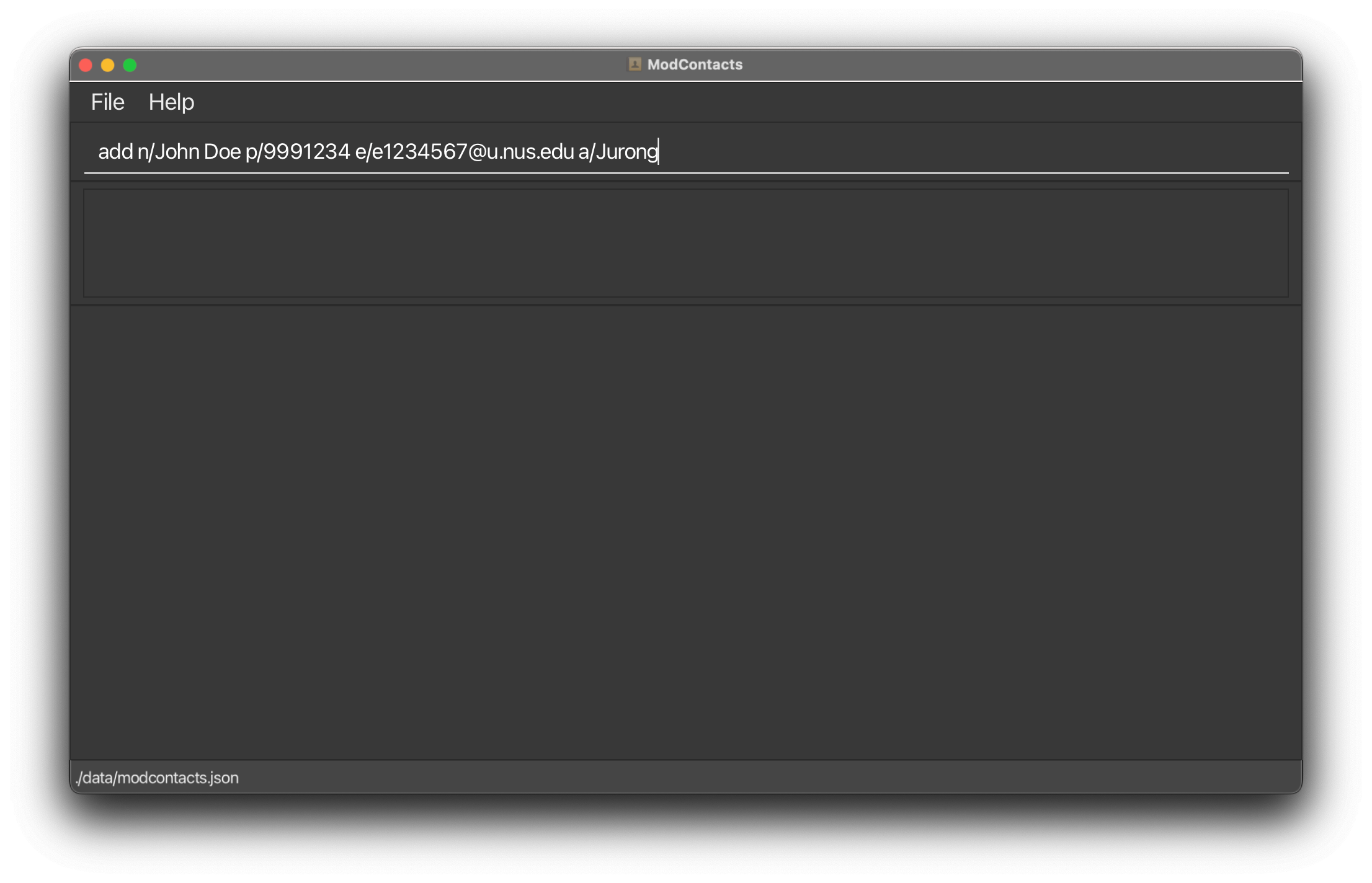
Suppose you want to add a friend with the following details:
- Name: John Doe
- Phone No: 9999 1234
- Email: e1234567@u.nus.edu
- Address: Jurong
Type the following command:
add n/John Doe p/9991234 e/e1234567@u.nus.edu a/Address
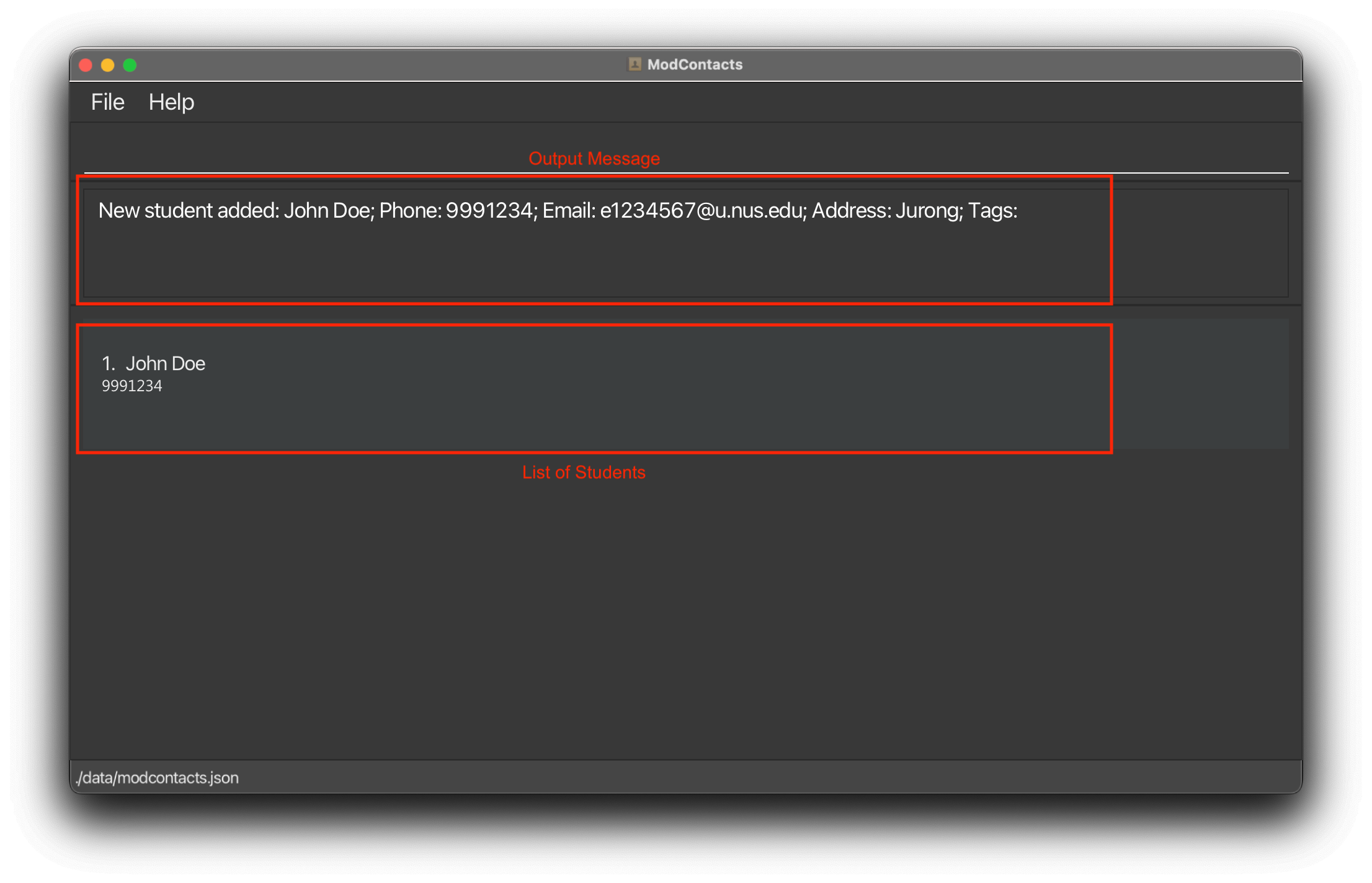
On Success
If the command is inputted the correctly, a message should appear informing you that the command was successful and a new entry is created.
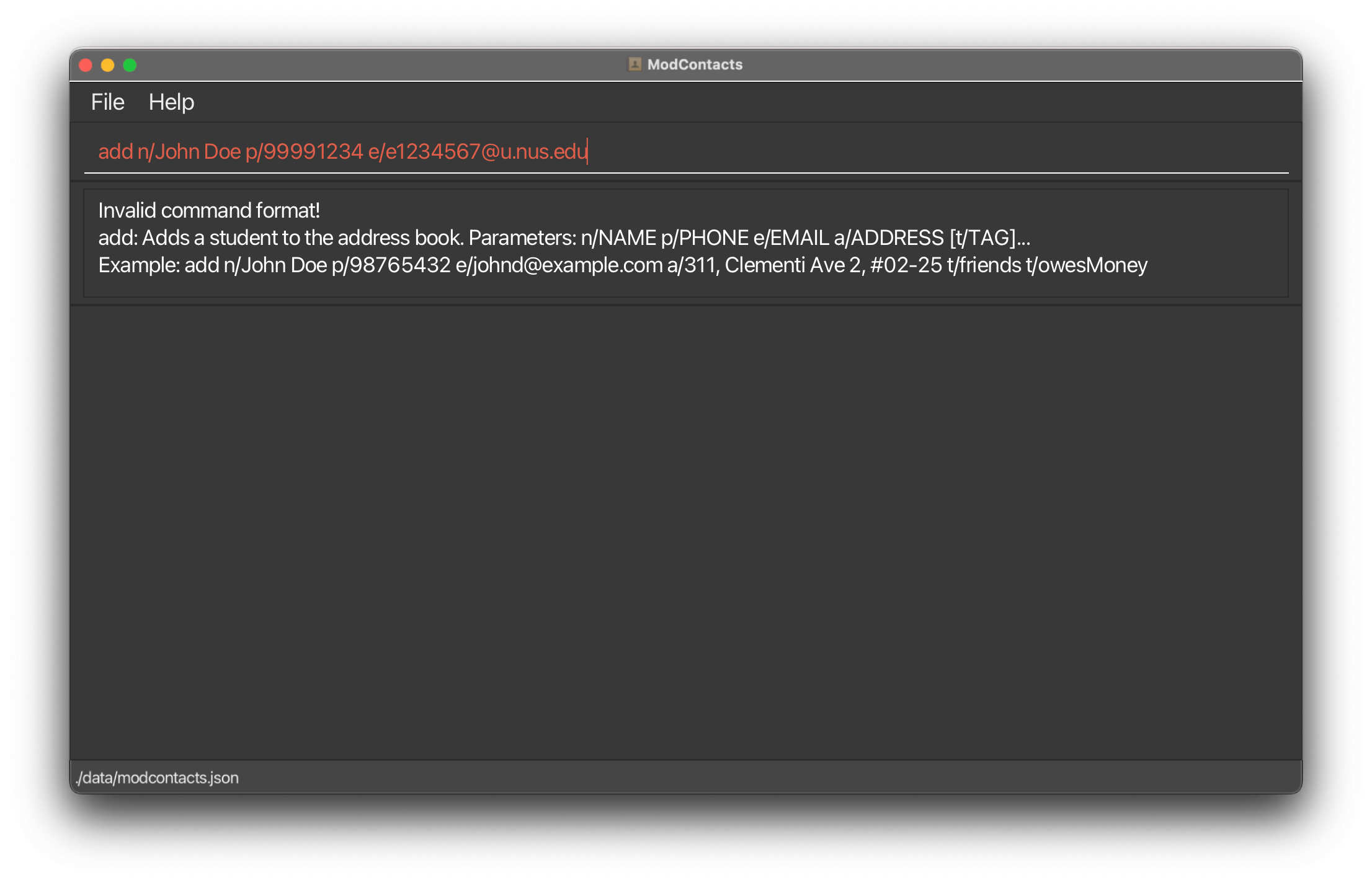
On Error
If the command is improperly formatted or certain parameters are missing the app will show what fields are needed and how a properly inputted command should look like.
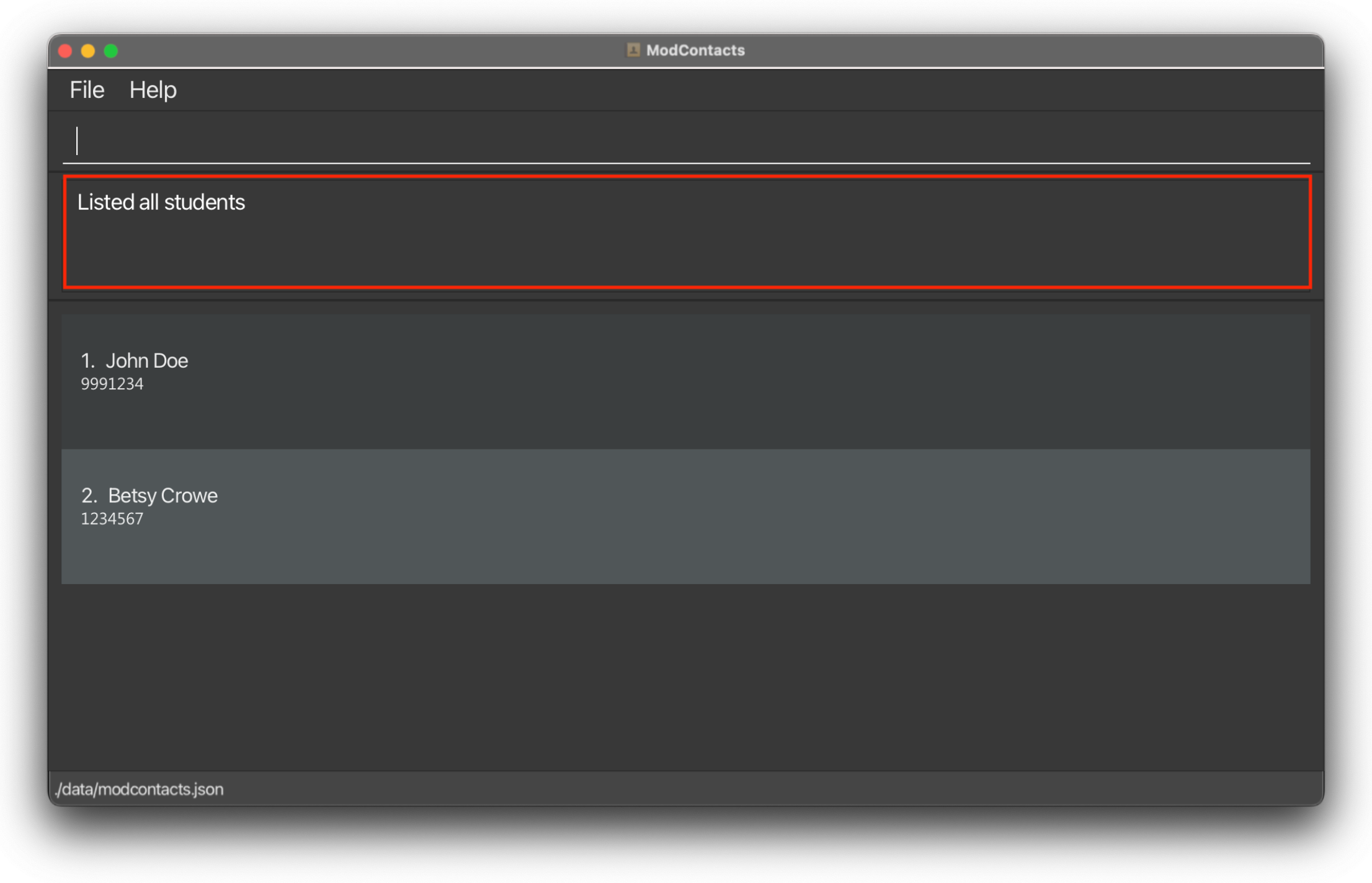
Listing all friends : list
Shows a list of all friends in the ModContacts list. You would need this command as sometimes you might commands (i.e find) which shows a filtered list instead of the entire list.
Format: list
On Success
A message should appear saying that all friends are being listed.
Editing a friend : edit
Edits an existing friend in the mod contacts list.
Format: edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…
- Edits the friend at the specified
INDEX. The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed friend list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - At least one of the optional fields must be provided.
- Existing values will be updated to the input values.
- When editing tags, the existing tags of the friend will be removed i.e adding of tags is not cumulative.
- You can remove all the friend’s tags by typing
t/without specifying any tags after it.
Examples:
-
edit 1 p/91234567 e/johndoe@example.comEdits the phone number and email address of the 1st friend to be91234567andjohndoe@example.comrespectively. -
edit 2 n/Betsy Crower t/Edits the name of the 2nd friend to beBetsy Crowerand clears all existing tags.
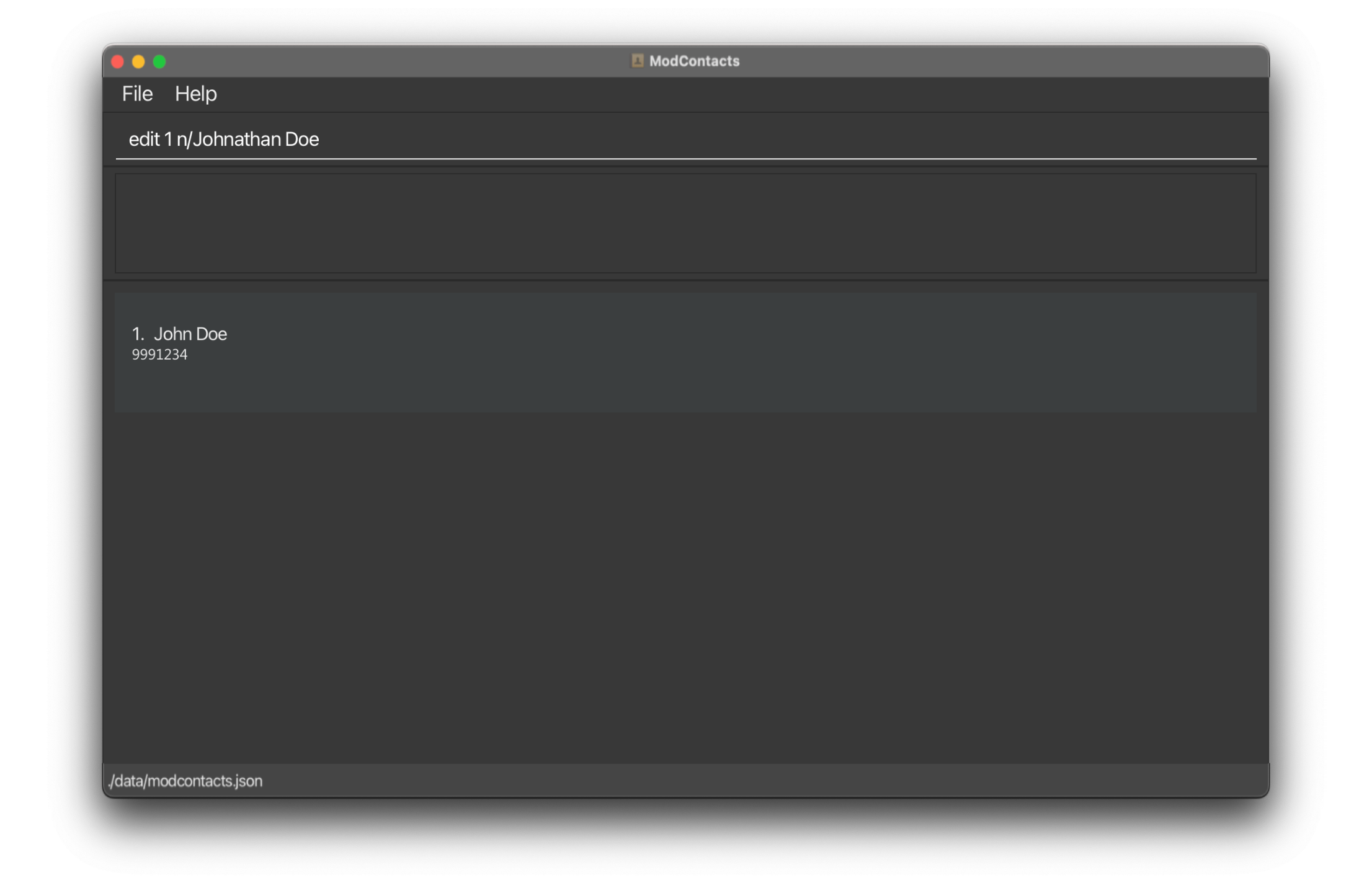
Before command
Suppose you want to edit a friend’s name (Like John Doe who we added in this add example)
Let’s change his name from John Doe to Johnathan Doe.
Type the following command:
edit 1 n/Johnathan Doe
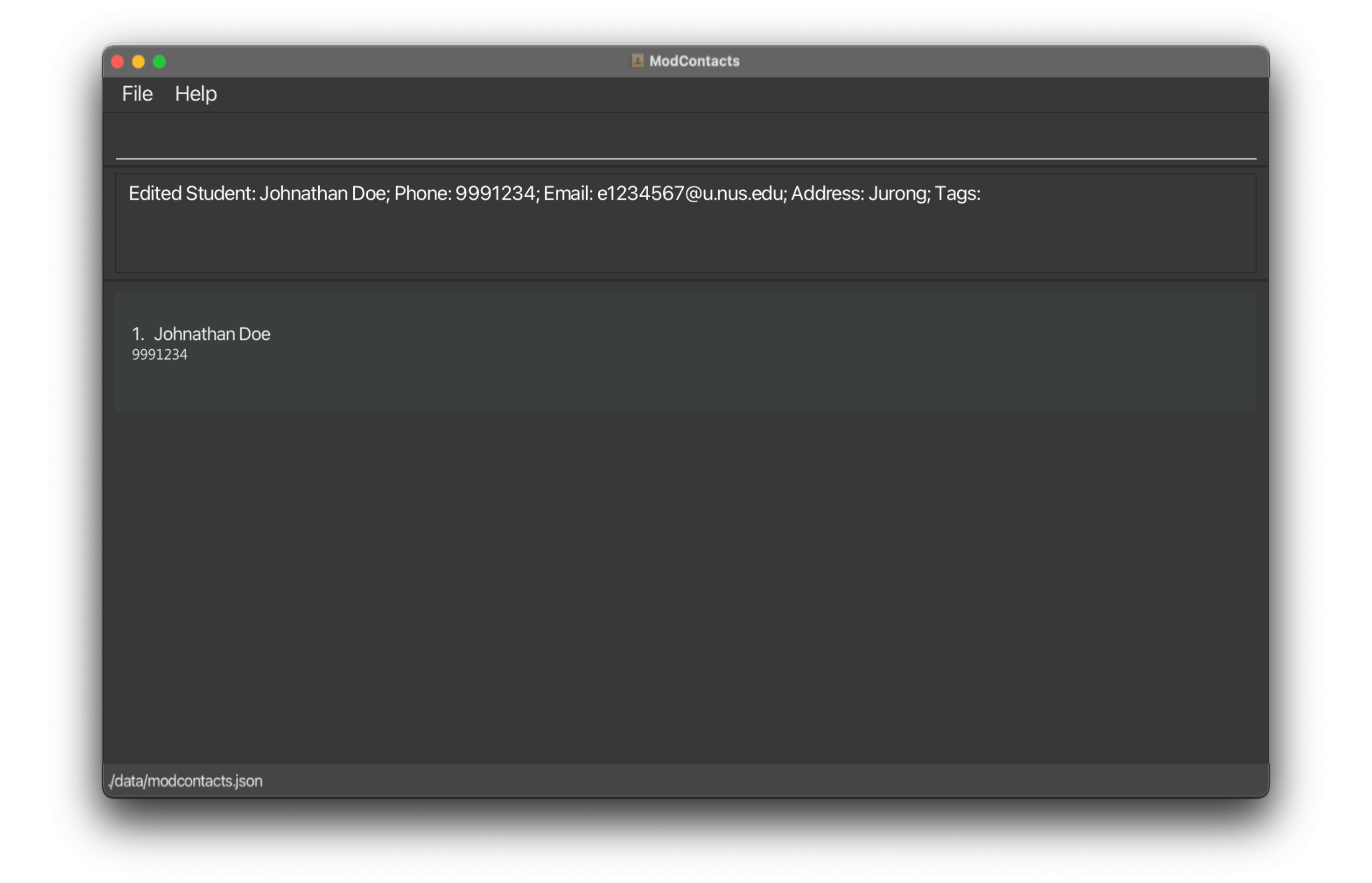
On Success
If the command is inputted the correctly, a message should appear informing you that the command was successful and your friend’s name has been edited.
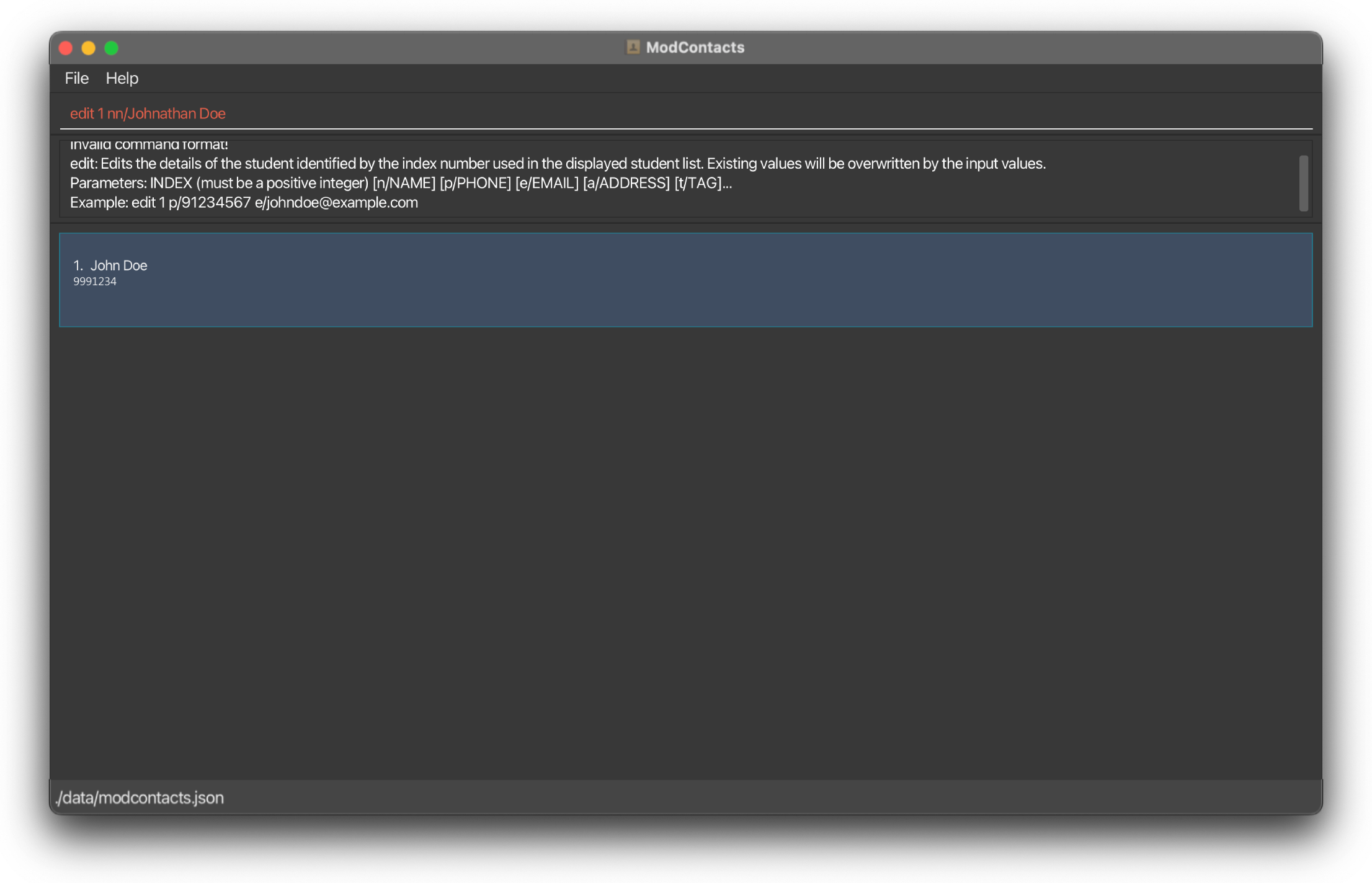
On Error
If the command is improperly formatted or certain parameters are missing the app will show what fields are needed and how a properly inputted command should look like. In this example we’ve accidentally written our name parameter as nn/.. instead of n/..
Adding a Module: add_module
Adds a module to your friend in the mod contacts list.
Format: add_module i/INDEX m/MODULE_CODE
- The
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed friend list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - The
MODULE_CODErefers to the module code of the module you intend to add
Examples:
-
add_module i/1 m/MA2001Adds the module MA2001 to the 1st friend
Before command
Suppose you want to add a module to the 1st friend on your list
Let’s add CS2101 to them!
Type the following command:
add_module i/1 m/CS2101
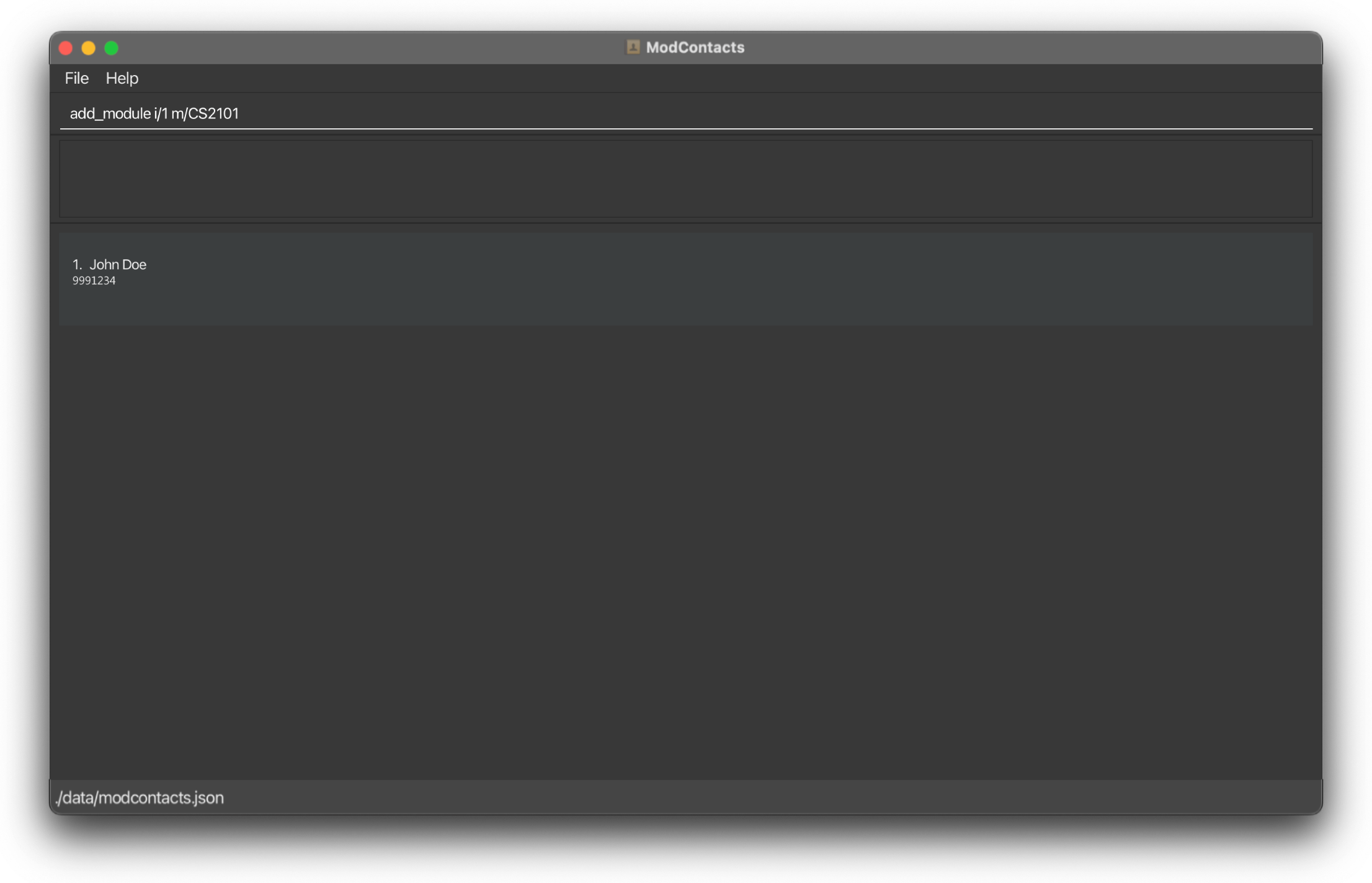
On Success
If the command is inputted the correctly, a message should appear informing you that the command was successful and the module has been added.
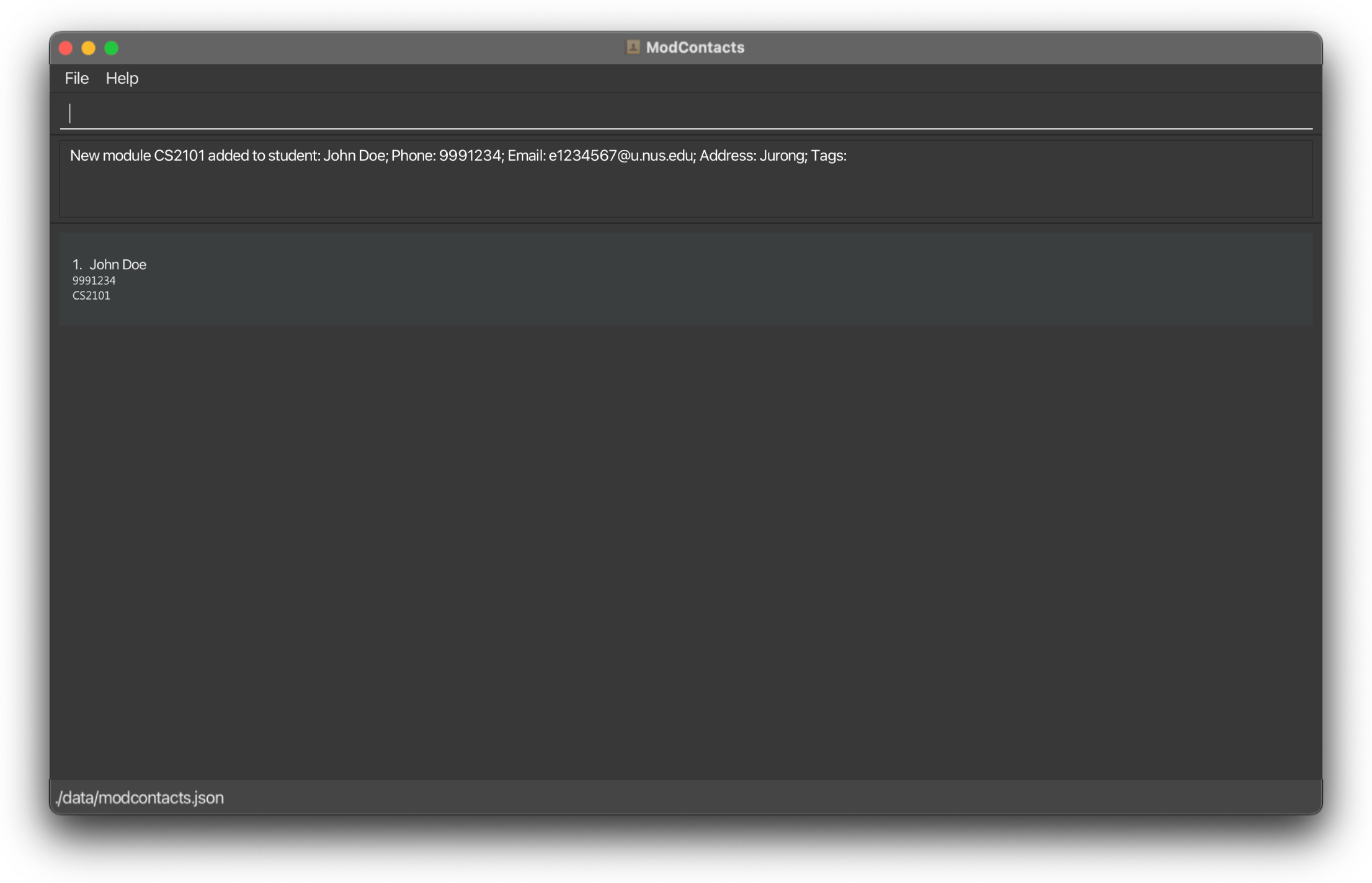
On Error
If the command is improperly formatted or certain parameters are missing the app will show what fields are needed and how a properly inputted command should look like. In this example we’ve added a non-existent module code MA200002.
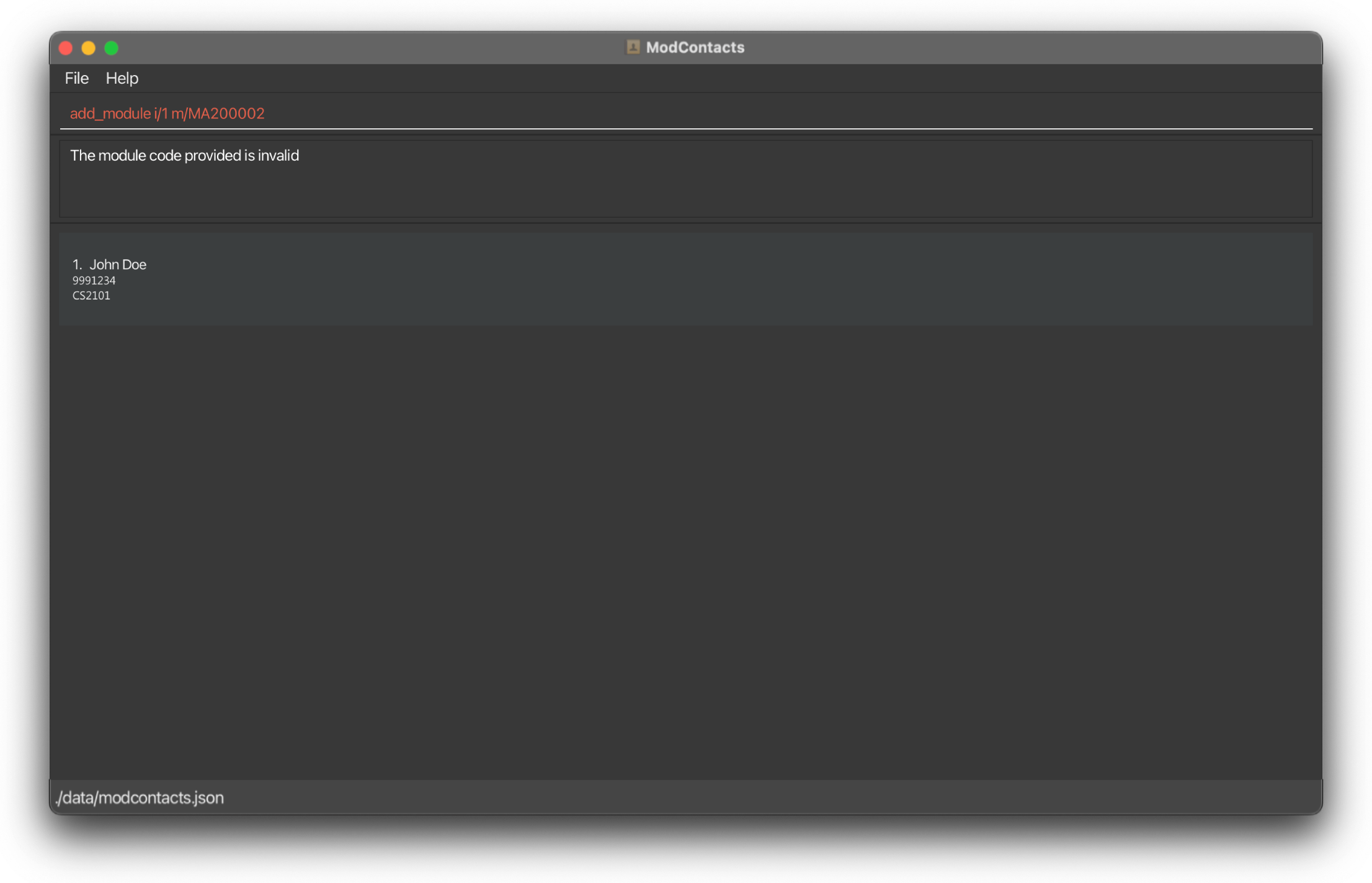
Deleting a Module: delete_module
Deletes a module from your friend in the mod contacts list.
Format: delete_module i/INDEX m/MODULE_CODE
- The
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed friend list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - The
MODULE_CODErefers to the module code of the module you intend to delete
Examples:
-
delete_module i/1 m/MA2001Deletes the module MA2001 to the 1st friend
Before command
Suppose you want to delete a module from the 1st friend on your list
Let’s remove CS2101
Type the following command:
delete_module i/1 m/CS2101
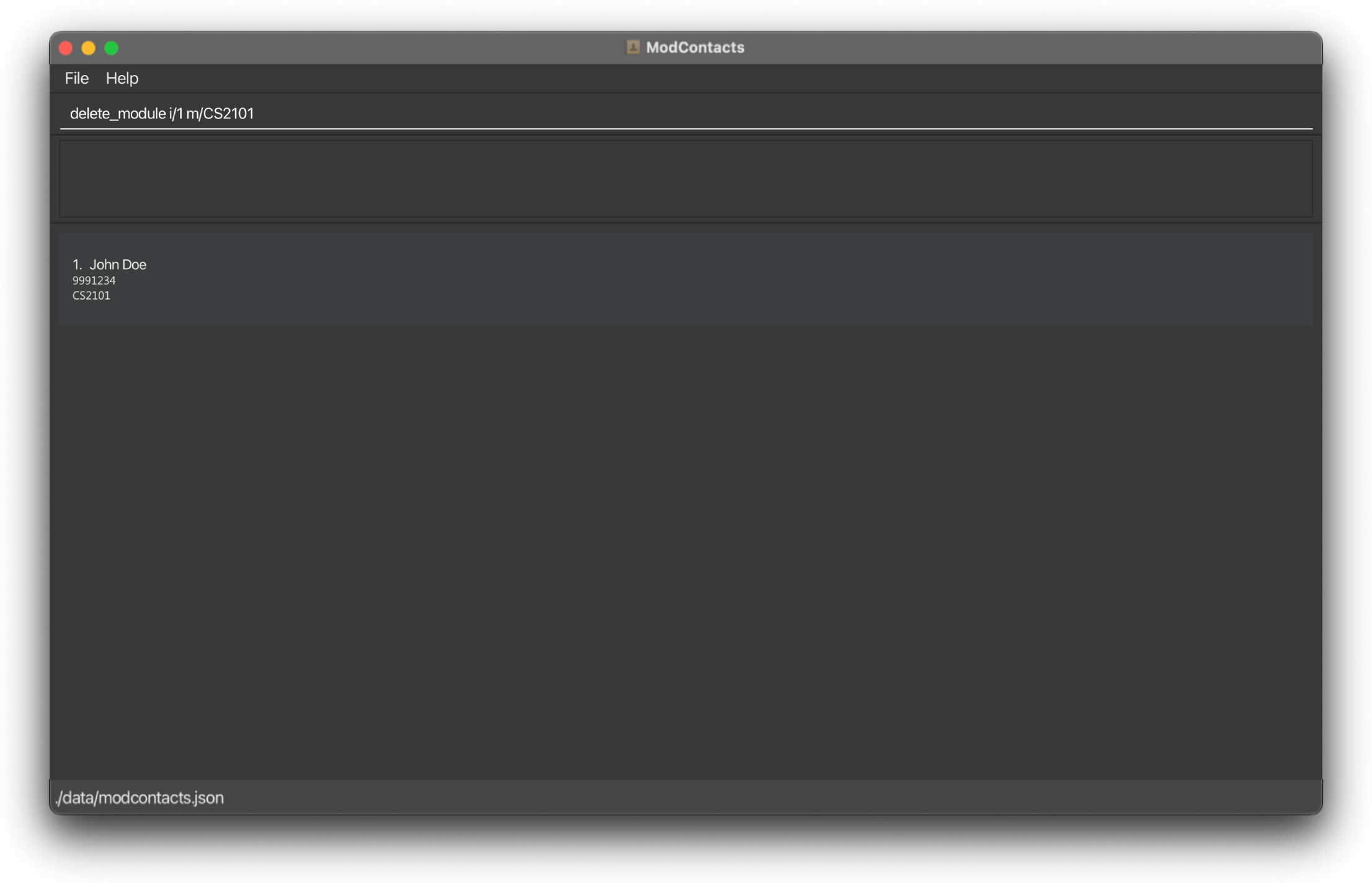
On Success
If the command is inputted the correctly, a message should appear informing you that the command was successful and the module has been deleted. The changes should be reflected on the list as well.
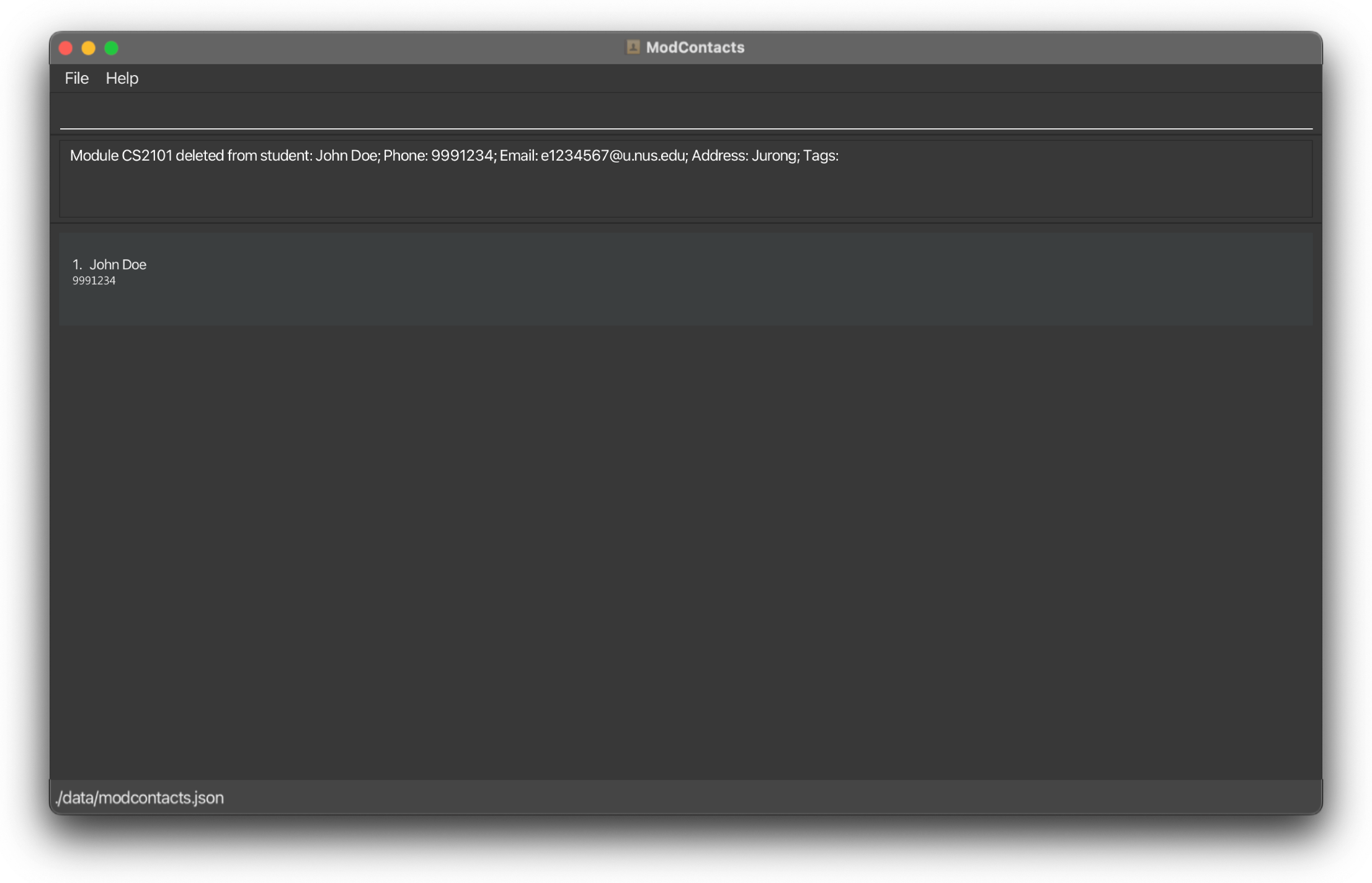
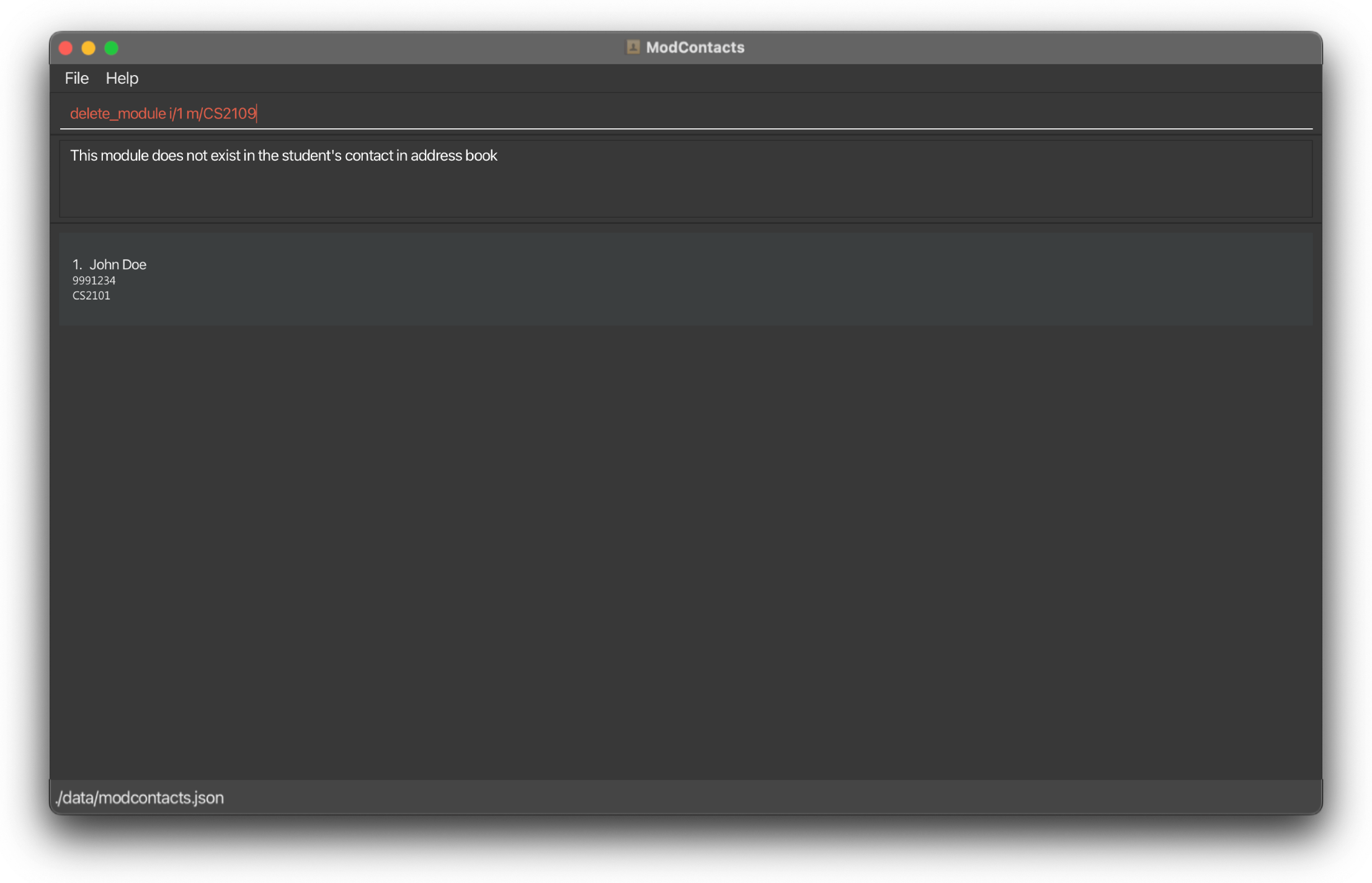
On Error
If the command is improperly formatted or certain parameters are missing the app will show what fields are needed and how a properly inputted command should look like. In this example we are trying to delete the module CS2109 which was never added to the friend.
Adding a Module Timing: add_timing
Adds a module’s class timing to your friend in the mod contacts list.
Format: add_timing i/INDEX m/MODULE_CODE d/DAY st/START_TIME et/END_TIME
- The
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed student list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - The
MODULE_CODErefers to the module code of the module you intend to add - The
DAYrefers to the day of the class, i.e. Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat, Sun (This is case-sensitive!) - The
START_TIMErefers to the start time of the class i.e. 0800, 1230, 1845, 2300 - The
END_TIMErefers to the end time of the class i.e. 0900, 1430, 2045, 2359
Examples:
-
add_timing i/1 m/MA2001 d/Mon st/1200 et/1400Adds a 1200h – 1400h timing for the module MA2001 to the 1st friend
Before command
Suppose you want to add the timing 1600h – 1800h to the CS2101 module for your 1st friend on the list
Type the following command:
add_timing i/1 m/CS2101 d/Wed st/1600 et/1800
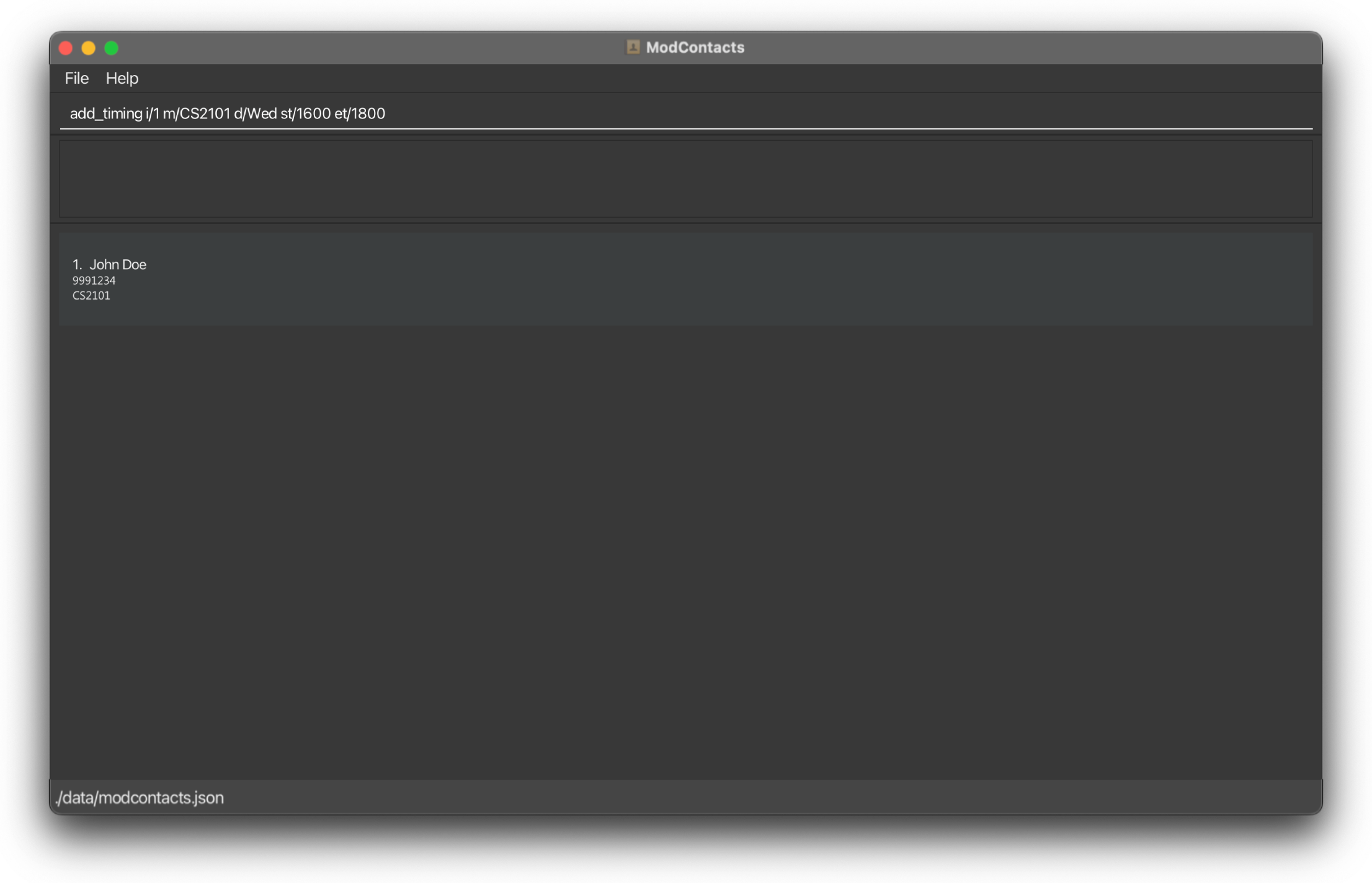
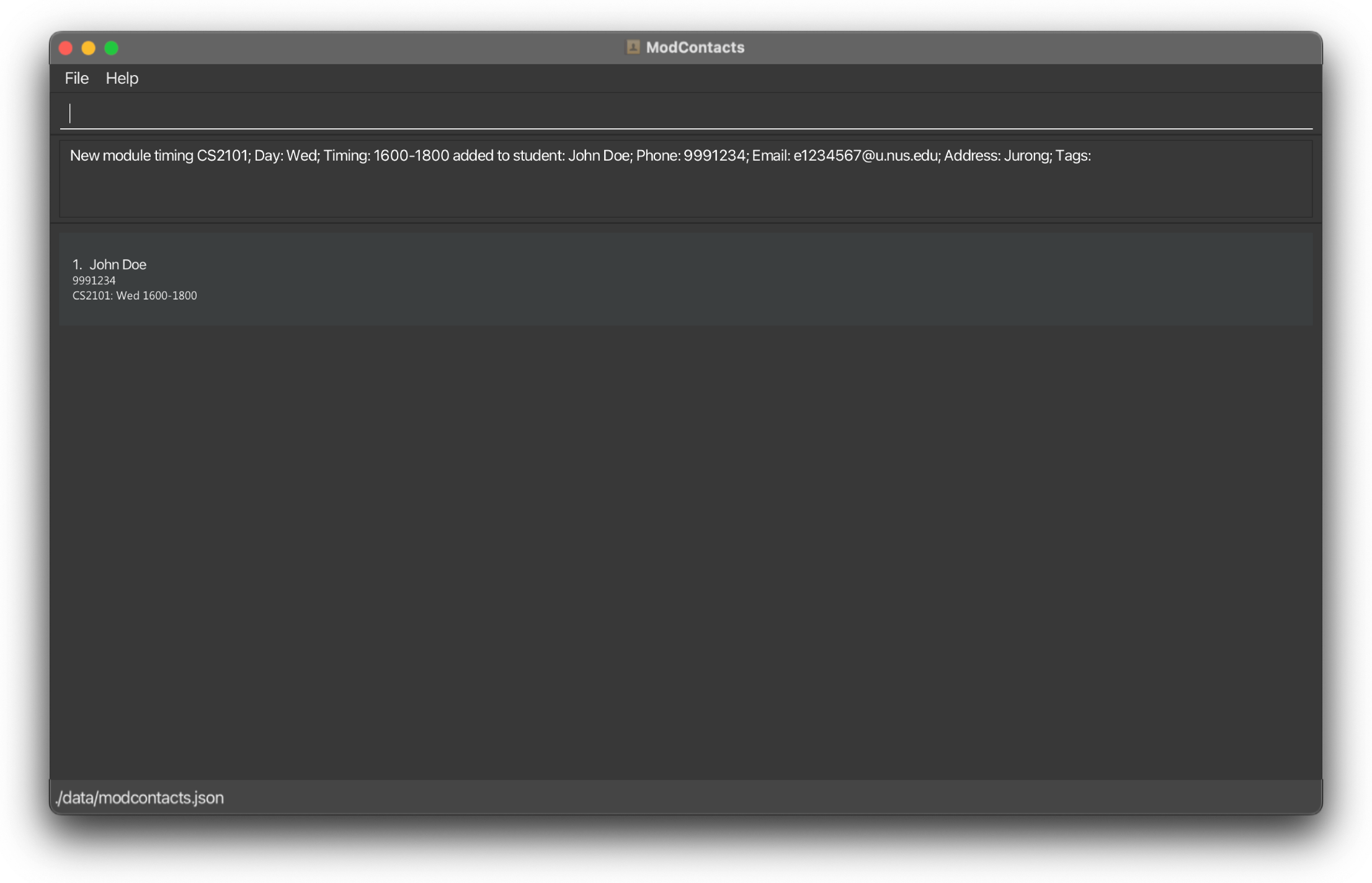
On Success
If the command is inputted the correctly, a message should appear informing you that the command was successful and the timing has been added. The changes should be reflected on the list as well.
On Error
If the command is improperly formatted or certain parameters are missing the app will show what fields are needed and how a properly inputted command should look like. In this example we used an incorrect time format (12h instead of 24h).
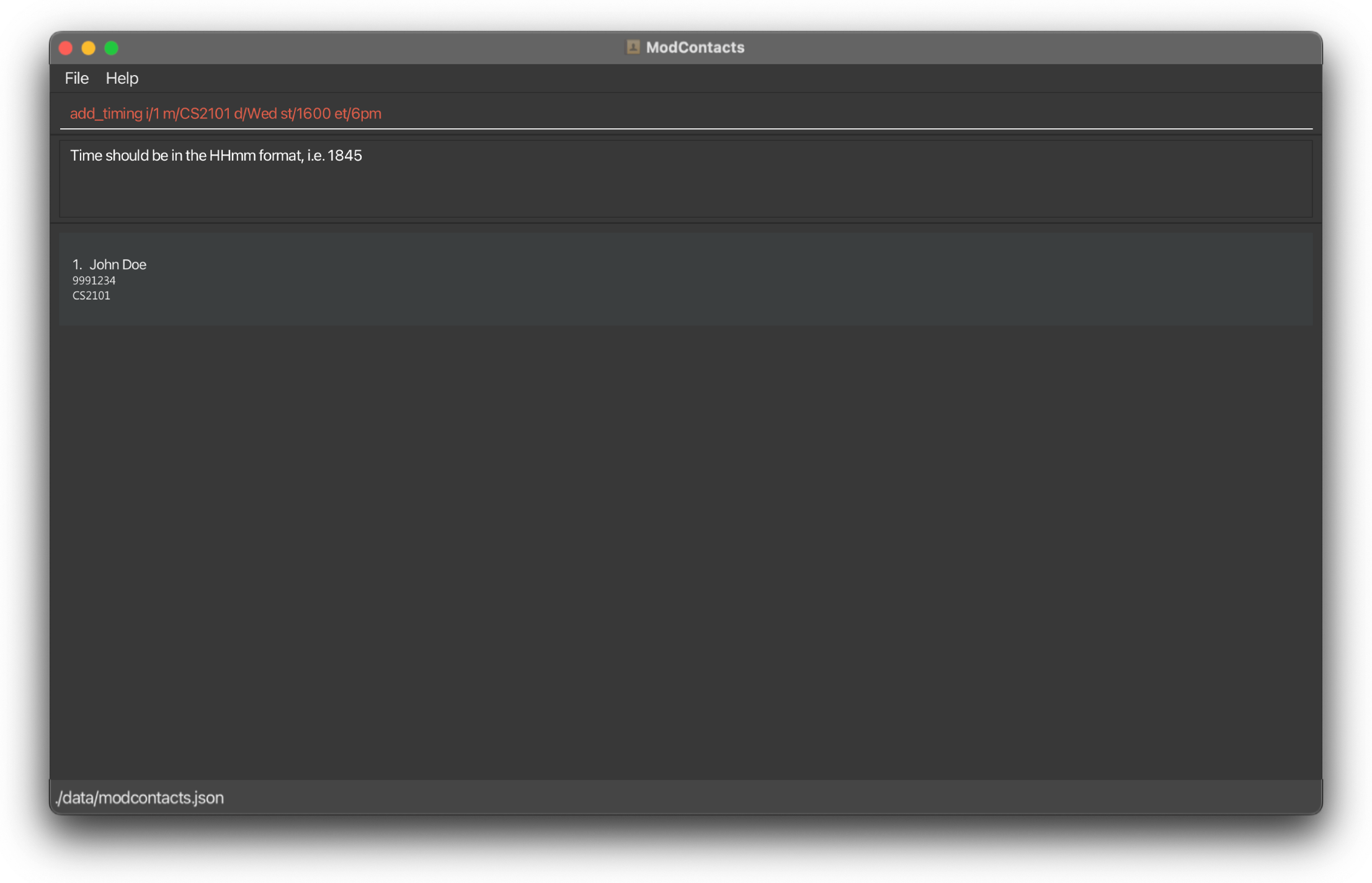
Deleting a Module Timing: delete_timing
Deletes a module’s class timing from your friend in the mod contacts list.
Format: delete_timing i/INDEX m/MODULE_CODE d/DAY st/START_TIME et/END_TIME
- The
INDEXrefers to the index number shown in the displayed student list. The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, … - The
MODULE_CODErefers to the module code of the module you intend to add - The
DAYrefers to the day of the class, i.e. Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat, Sun (This is case-sensitive!) - The
START_TIMErefers to the start time of the class i.e. 0800, 1230, 1845, 2300 - The
END_TIMErefers to the end time of the class i.e. 0800, 1230, 1845, 2300
Examples:
-
delete_timing i/1 m/MA2001 d/Mon st/1200 et/1400Deletes the 1200h – 1400h timing for the module MA2001 to the 1st friend
Before command
Suppose you want to delete the timing 1600h – 1800h to the CS2101 module for your 1st friend on the list
Type the following command:
delete_timing i/1 m/CS2101 d/Wed st/1600 et/1800
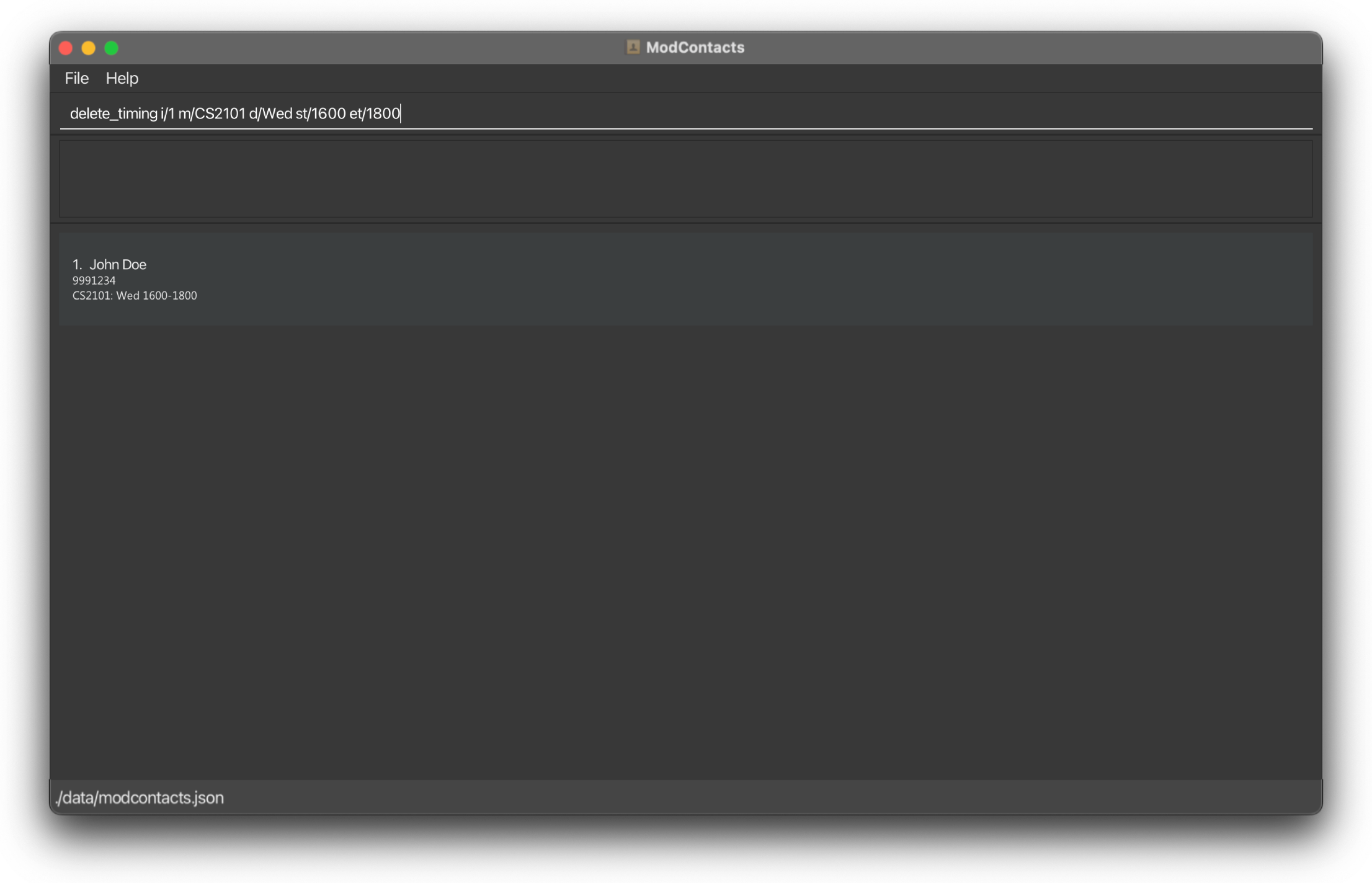
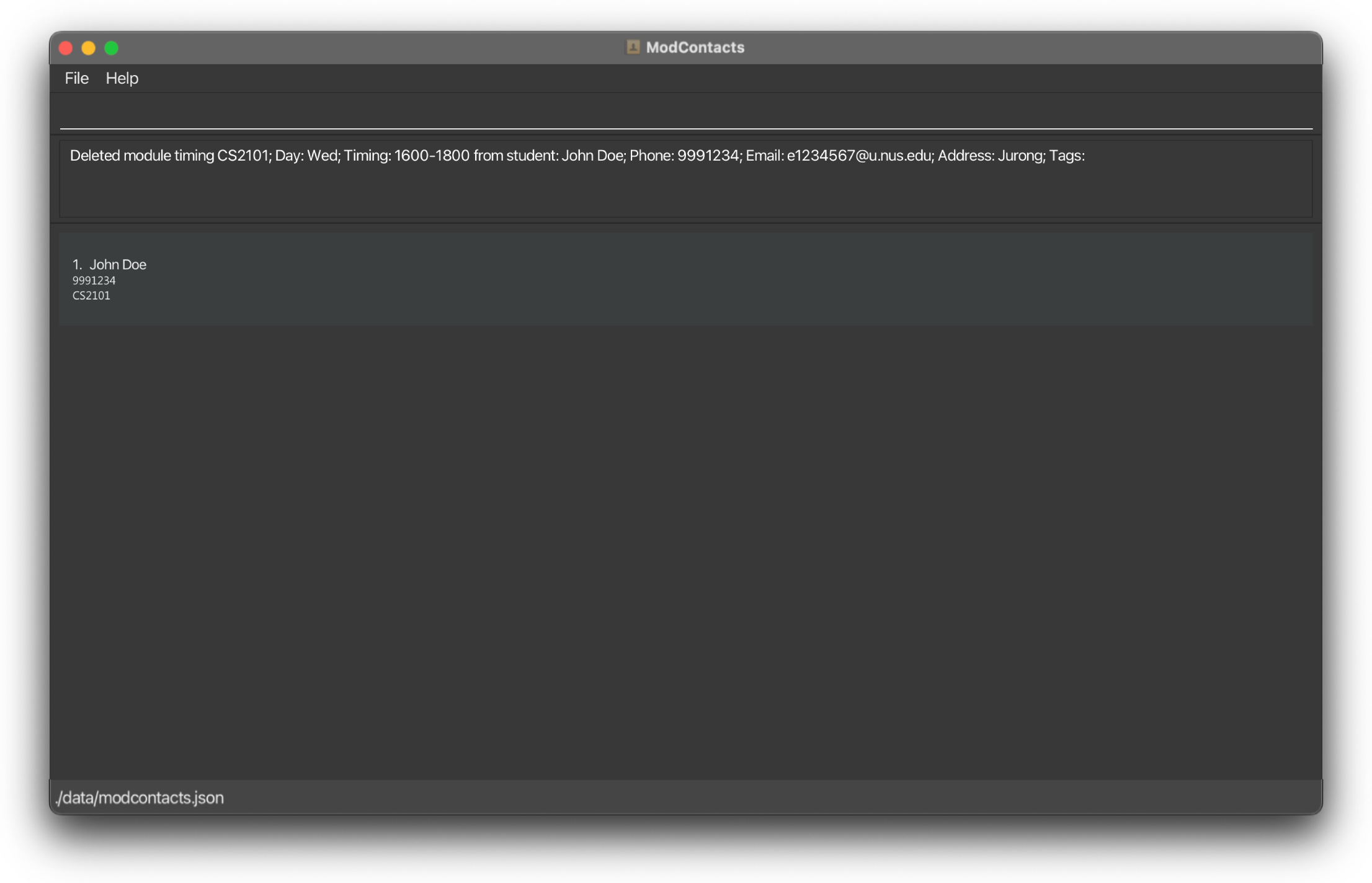
On Success
If the command is inputted the correctly, a message should appear informing you that the command was successful and the timing has been deleted. The changes should be reflected on the list as well.
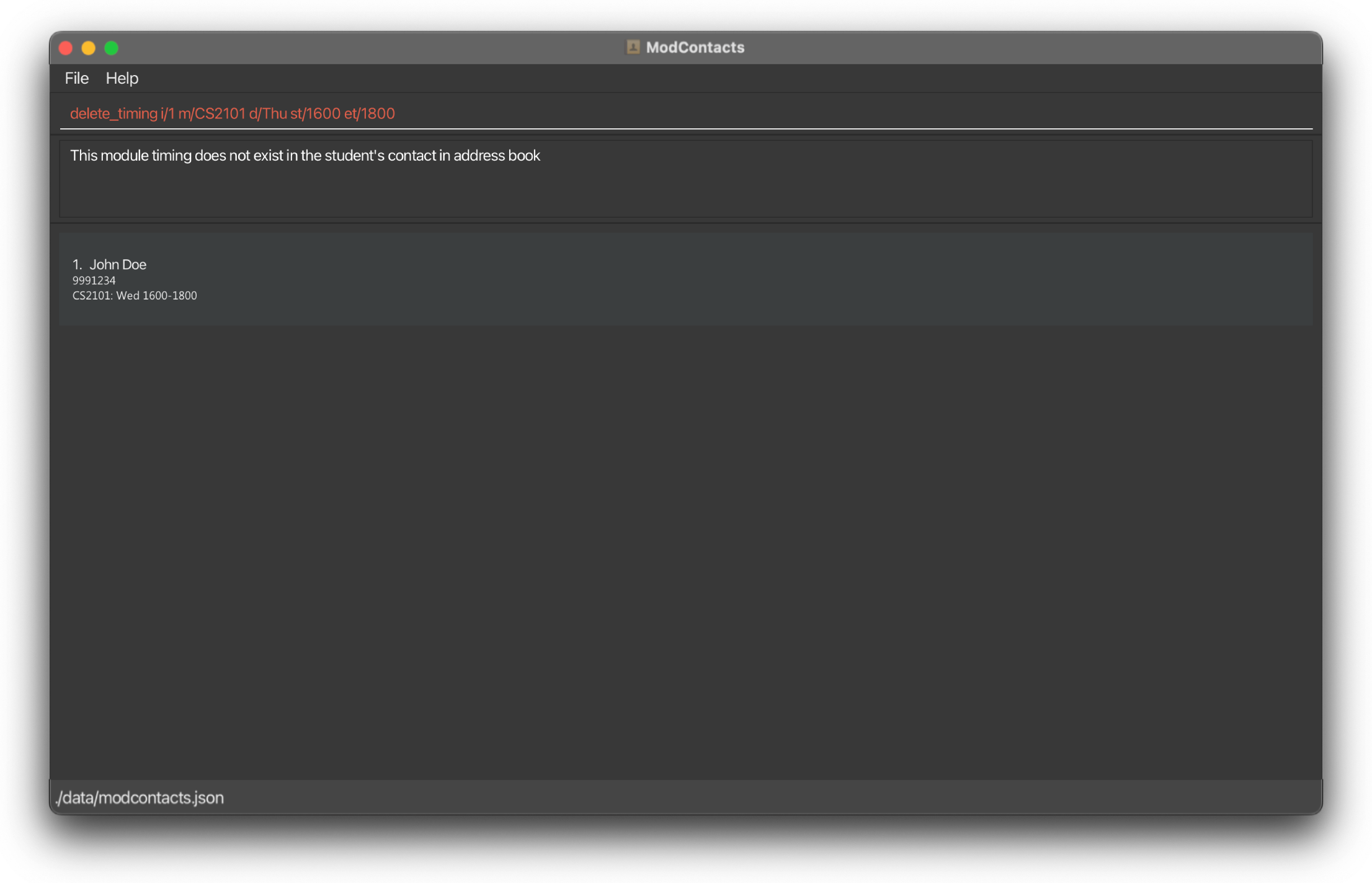
On Error
If the command is improperly formatted or certain parameters are missing the app will show what fields are needed and how a properly inputted command should look like. In this example we inputted the wrong day (It should be Wed and not Thu) for the timing that we previously added.
Locating friends by name: find
Finds friends whose names contain any of the given keywords.
Format: find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]
- The search is case-insensitive. e.g
hanswill matchHans - The order of the keywords does not matter. e.g.
Hans Bowill matchBo Hans - Only the name is searched.
- Only full words will be matched e.g.
Hanwill not matchHans - Friends matching at least one keyword will be returned (i.e.
ORsearch). e.g.Hans Bowill returnHans Gruber,Bo Yang
Examples:
-
find JohnFinds a friend whose name containsJohn
Before command
Suppose you want to find your friend John Doe
Type the following command:
find John
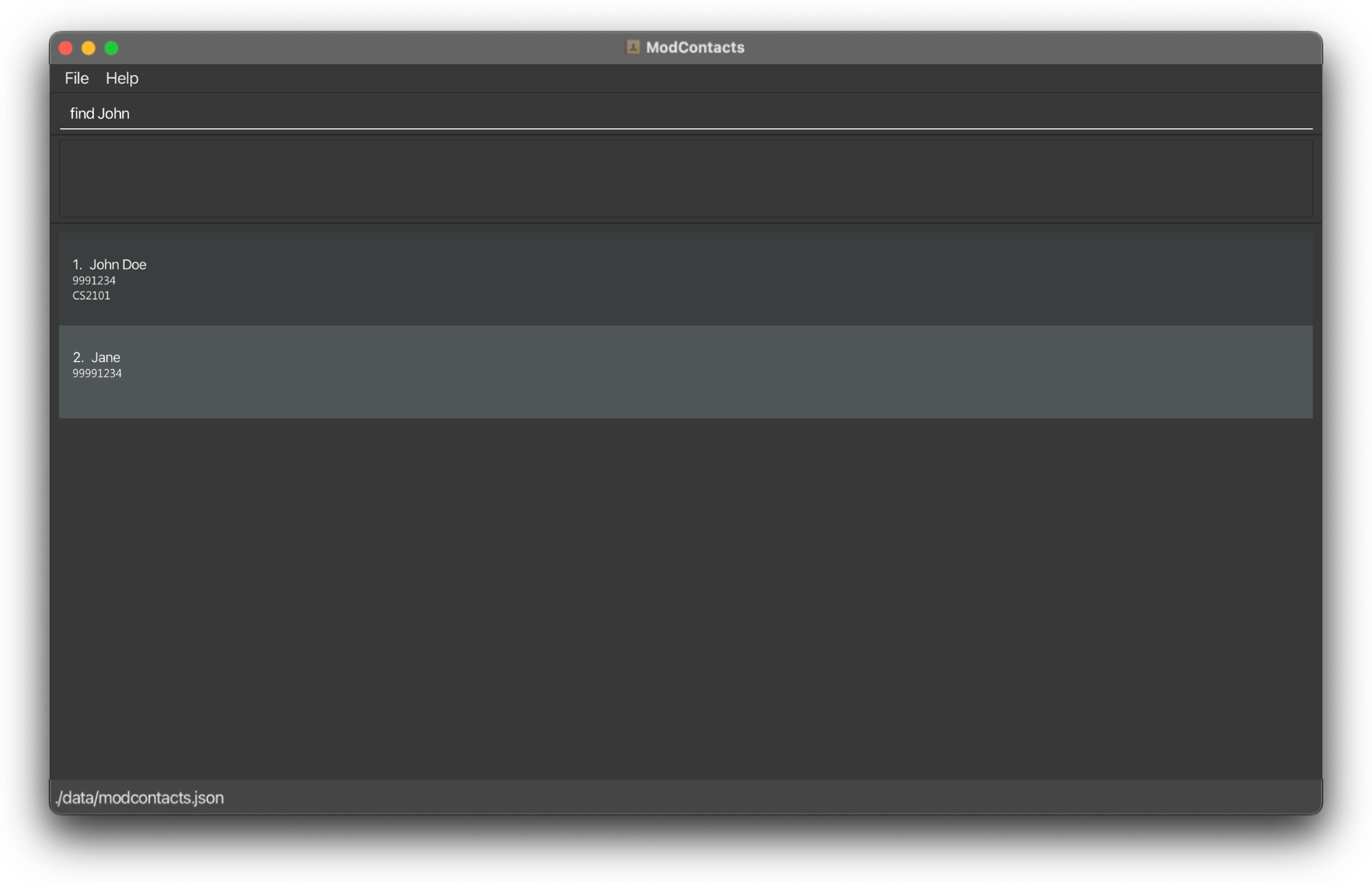
On Success
If the command is inputted the correctly, a message should appear informing you that the command was successful and how many friends whose names contains the keyword you are searching. A filtered list will then be shown showing who matches the name you are searching for.
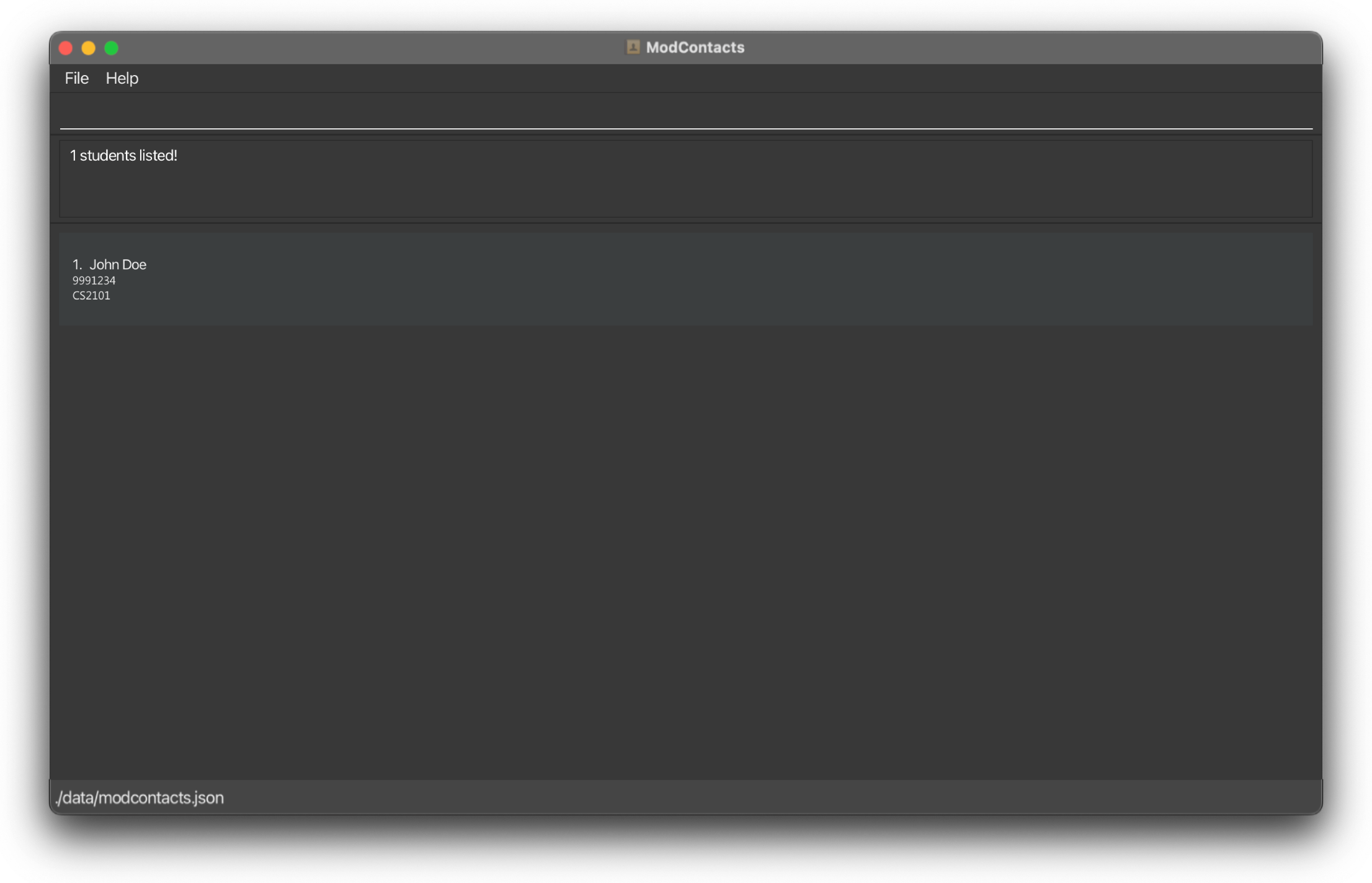
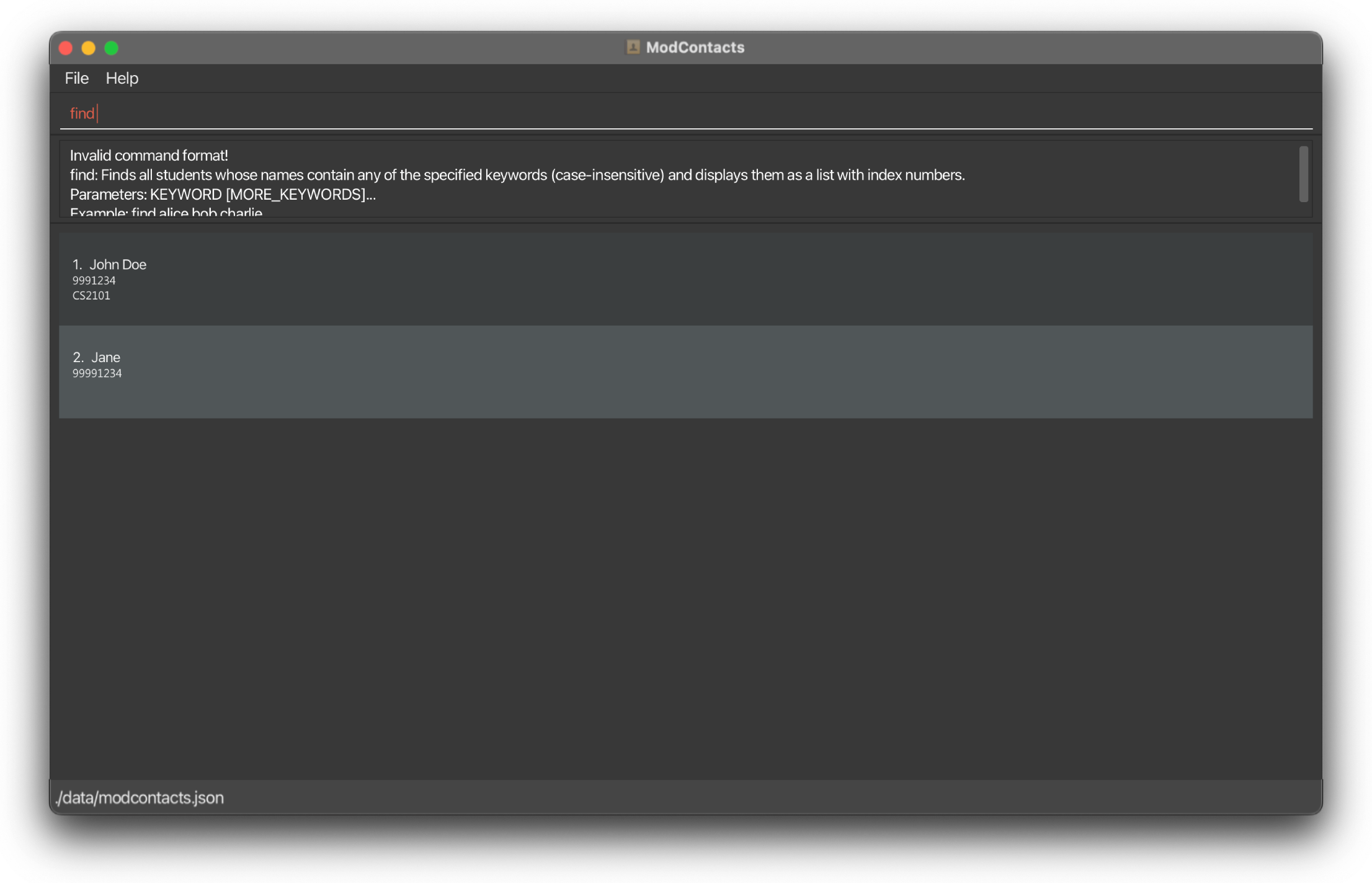
On Error
If the command is improperly formatted or certain parameters are missing the app will show what fields are needed and how a properly inputted command should look like. In this example we did not include the keyword to search for.
Find friends who are free to meet: find_free_time
Finds friends who are free at this given time period.
Format: find_free_time d/DAY st/START_TIME et/END_TIME
- The
DAYrefers to the day of the class, i.e. Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, Fri, Sat, Sun (This is case-sensitive!) - The
START_TIMErefers to the start time of the class i.e. 0800, 1230, 1845, 2300 - The
END_TIMErefers to the end time of the class i.e. 0900, 1430, 2045, 2359
Examples:
-
find_free_time d/Wed st/1500 et/1600Find a list of friends who are free on Wednesday 1500h – 1600h
Before command
Suppose you are free on Monday 1200h – 1300h and you would like to find out which friends are free as well.
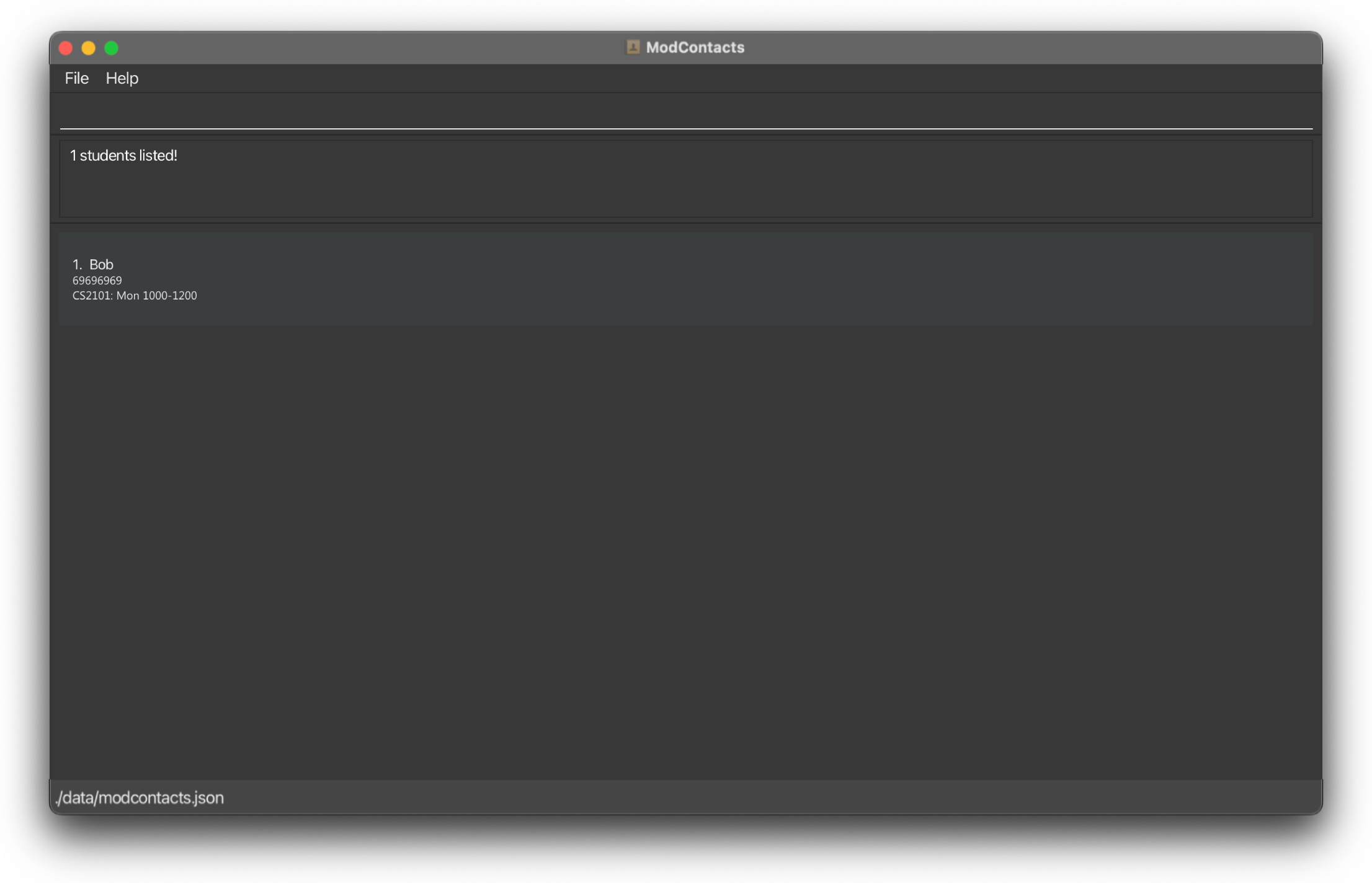
Your two friends Alice and Bob are on ModContacts and these are their current schedules on Monday.
-
Alicehas a lesson from 1000h - 1200h -
Bobhas a lesson from 1100h - 1300h

Type the following command:
find_free_time d/Mon st/1200 et/1300
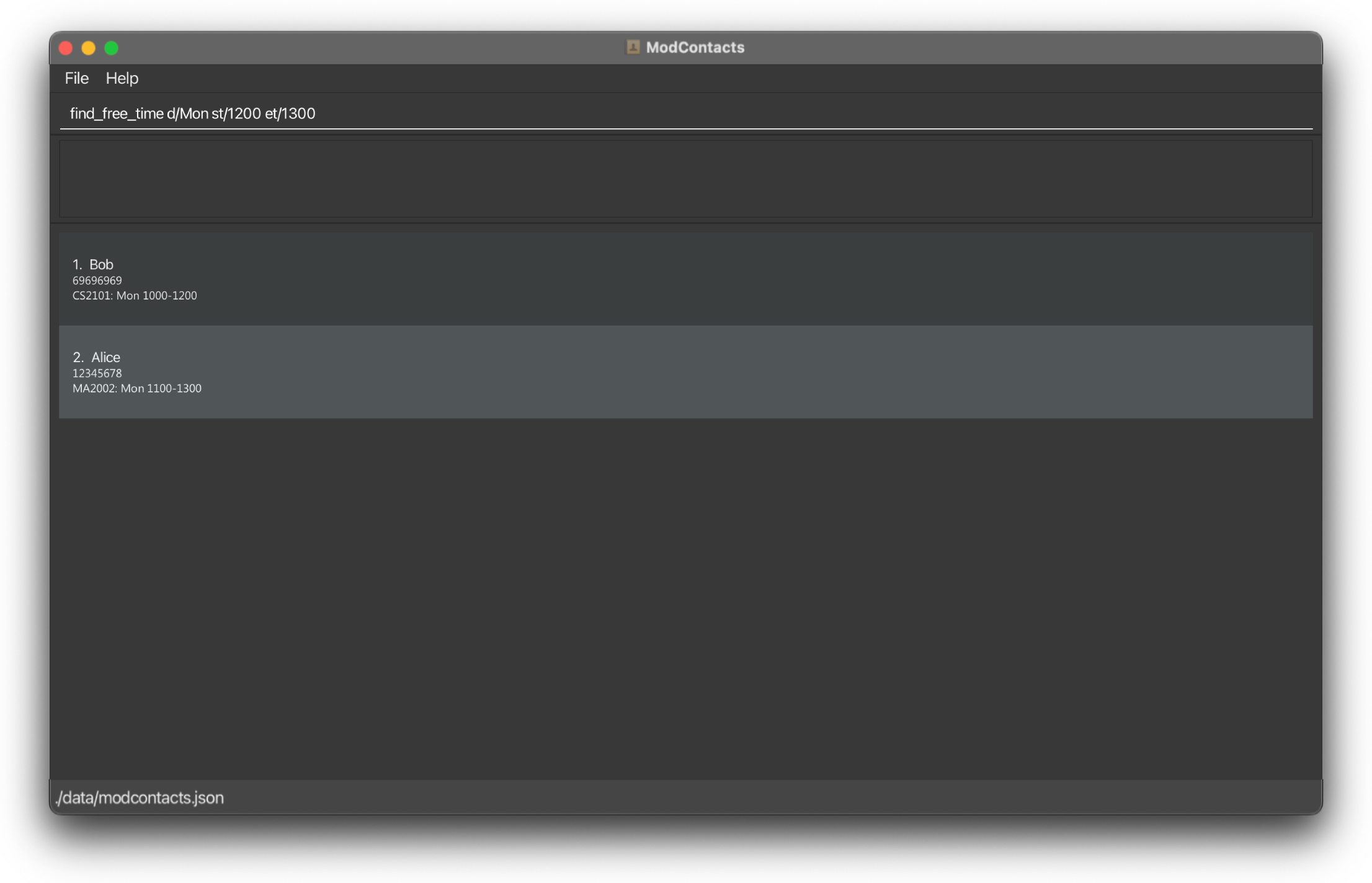
On Success
If the command is inputted the correctly, a message should appear informing you that the command was successful and how many friends whose names contains the keyword you are searching. A filtered list will then be shown showing which friends are free in the stipulated time.
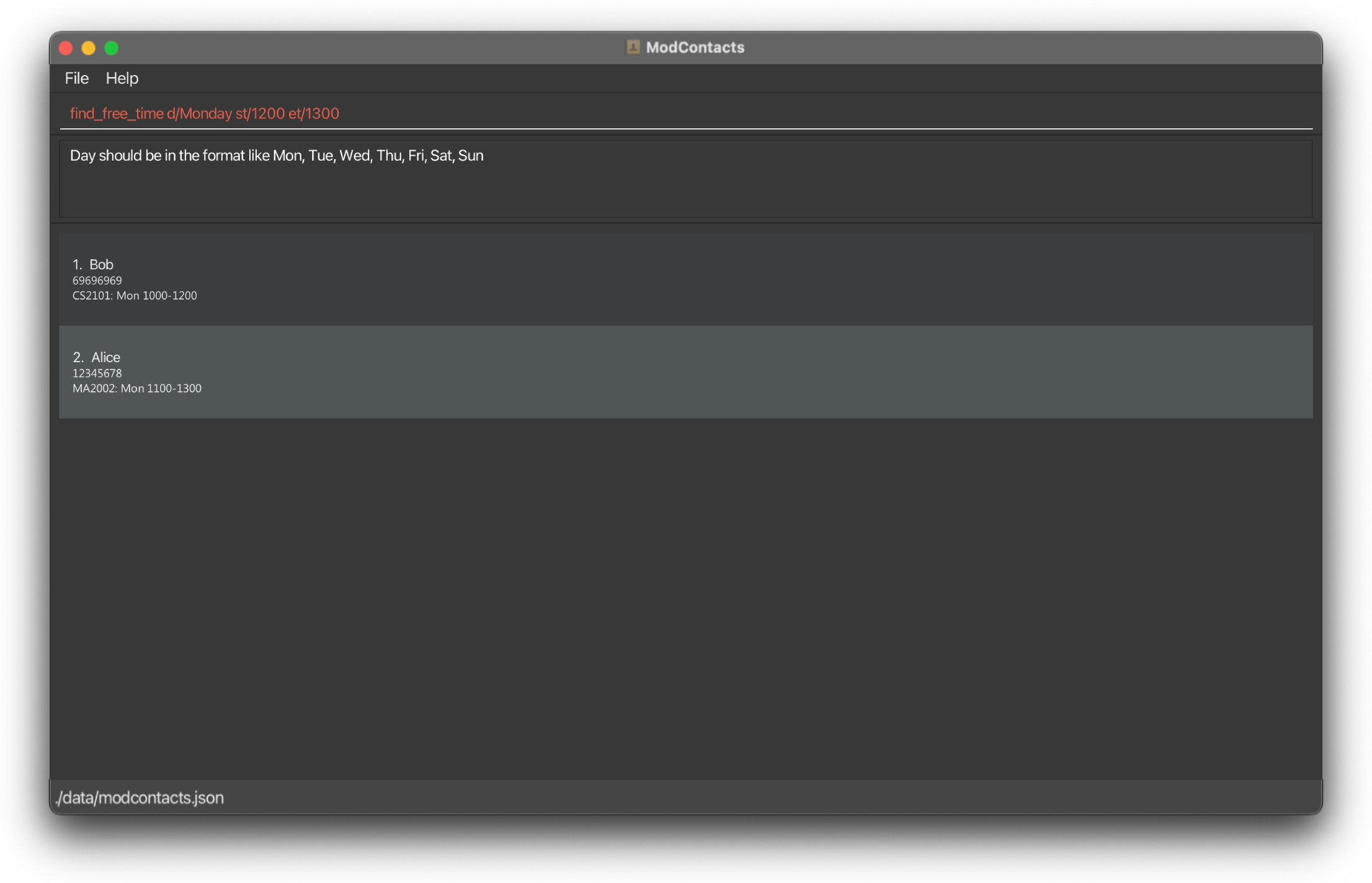
On Error
If the command is improperly formatted or certain parameters are missing the app will show what fields are needed and how a properly inputted command should look like. In this example we did not key in the day in the proper format (Monday instead of Mon)
Learn more about modules: list_modules
List Modules allows you to search for the available modules in NUS and get its description.
Format: list_modules m/MODULE_CODE
- The
MODULE_CODErefers to the prefix or the first few characters of the module you intend to search. This search case insensitive, which means searching withm/CS2103andm/cs2103will yield the same results.
For example, you can search for all modules starting with CS21 with the command list_modules m/cs21 and it will list all modules in NUS starting with the given module code.

[MODULE_CODE]” will be displayed.
Find friends with modules: module_search
Looking for buddies to discuss schoowork? Finds friends who are taking the specified module.
Format: module_search m/MODULE_CODE
- The
MODULE_CODErefers to the FULL module you intend to search. This iscase insensitive, which means searching withm/CS2103Tandm/cs2103Twill yield the same results.
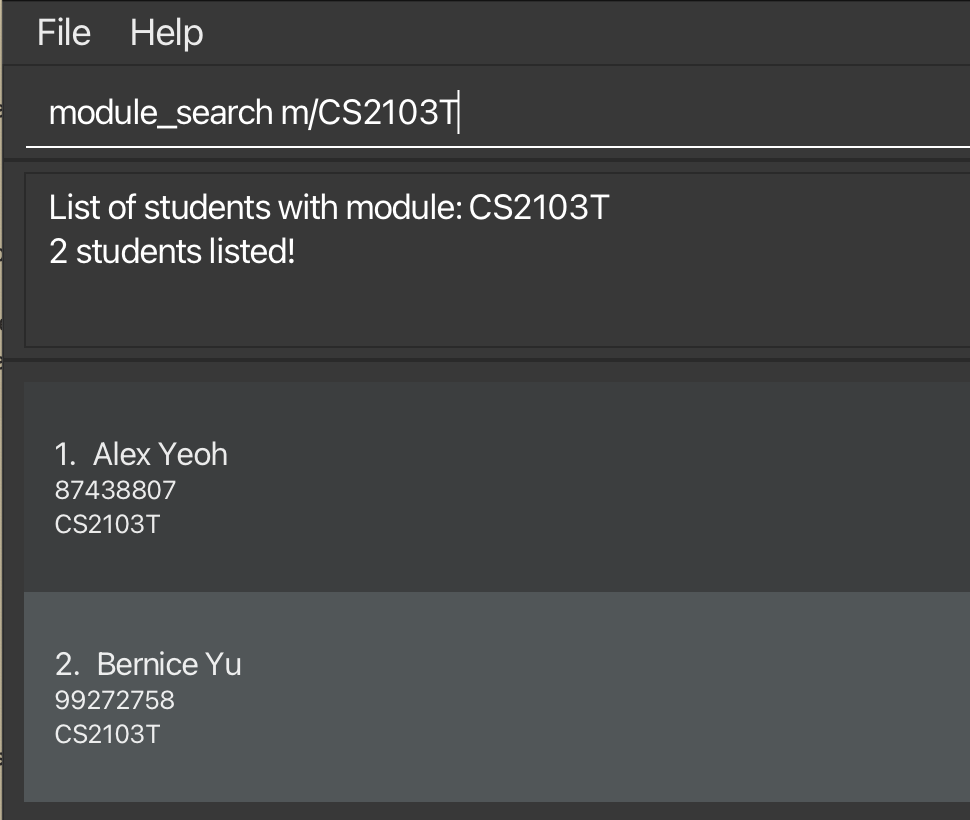
list_modules command.
Deleting a friend : delete
Deletes the specified friend from the mod contacts list.
Format: delete INDEX
- Deletes the friend at the specified
INDEX. - The index refers to the index number shown in the displayed friend list.
- The index must be a positive integer 1, 2, 3, …
Examples:
-
listfollowed bydelete 2deletes the 2nd friend in the mod contacts list. -
find Betsyfollowed bydelete 1deletes the 1st friend in the results of thefindcommand.
Clearing all entries : clear
Clears all entries from the mod contacts list.
Format: clear
Exiting the program : exit
Exits the program.
Format: exit
FAQ
Q: How do I transfer my data to another Computer?
A: Install the app in the other computer and overwrite the empty data file it creates with the file that contains the data of your previous ModContacts home folder.
Q: How do I know if my data is saved?
A: ModContacts data are saved in the hard disk automatically after any command that changes the data. There is no need to save manually.
Q: Can I manually edit the data file?
A: ModContacts data are saved automatically as a JSON file [JAR file location]/data/modcontacts.json. Advanced users are welcome to update data directly by editing that data file.
Furthermore, certain edits can cause the ModContacts to behave in unexpected ways (e.g., if a value entered is outside of the acceptable range). Therefore, edit the data file only if you are confident that you can update it correctly.
Glossary
| Glossary Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| CLI | Command Line Interface, the text-based interface for interacting with ModContacts. |
| GUI | Graphical User Interface, the visual interface for interacting with ModContacts. |
| Command | The instruction given to ModContacts to perform a specific action. |
| Prefix | A 1 letter keyword, with a / at the end, such as m/, i/ that is used to specify the type of data for the command. |
| NUS | National University of Singapore, the university that ModContacts is designed for. |
| SoC | School of Computing, the faculty in NUS that ModContacts is designed for. |
| field | A piece of information that can be added to a command. e.g. n/John Doe has the field John Doe, with the prefix n/. |
| camel casing | A casing format where words are not separated by whitespaces. Words are joined together and the first letter of each word, except the first one, is capital. Example: “thisIsCamelCasing” is “this is camel casing” in camel casing. |
Known issues
-
When using multiple screens, if you move the application to a secondary screen, and later switch to using only the primary screen, the GUI will open off-screen. The remedy is to delete the
preferences.jsonfile created by the application before running the application again.
Command summary
| Action | Format, Examples |
|---|---|
| Help | help |
| Add |
add n/NAME p/PHONE_NUMBER e/EMAIL a/ADDRESS [t/TAG]… e.g., add n/James Ho p/22224444 e/jamesho@example.com a/123, Clementi Rd, 1234665 t/friend t/colleague
|
| List | list |
| Edit |
edit INDEX [n/NAME] [p/PHONE_NUMBER] [e/EMAIL] [a/ADDRESS] [t/TAG]…e.g., edit 2 n/James Lee e/jameslee@example.com
|
| Delete |
delete INDEXe.g., delete 3
|
| Add Module |
add_module i/INDEX m/MODULE_CODEe.g., add_module i/1 m/CS2103T
|
| Delete Module |
delete_module i/INDEX m/MODULE_CODEe.g., delete_module i/1 m/MA2001
|
| Add Timing |
add_timing i/INDEX m/MODULE_CODE d/DAY st/START_TIME et/END_TIMEe.g., add_timing i/1 m/MA2001 d/Mon st/1200 et/1400
|
| Delete Timing |
delete_timing i/INDEX m/MODULE_CODE d/DAY st/START_TIME et/END_TIMEe.g., delete_timing i/1 m/MA2001 d/Mon st/1200 et/1400
|
| Find |
find KEYWORD [MORE_KEYWORDS]e.g., find James Jake
|
| Find Free Timing |
find_free_time d/DAY st/START_TIME et/END_TIMEe.g., find_free_time d/Wed st/1500 et/1600
|
| List Modules |
list_modules m/MODULE_CODE e.g. list_modules m/cs21
|
| Search Module |
search m/MODULE_CODE e.g. search m/CS2103T
|
| Clear | clear |
| Exit | exit |